What is agile project management?
Agile project management is an iterative and collaborative approach where a project is delivered in increments across its lifecycle. In agile project management, work is split into sizable and manageable chunks, known as sprints, which are completed at intervals over one to six weeks. The agile approach emphasizes active collaboration through customer feedback loops, flexibility to change, continuous improvement in product development, and quick delivery of potentially shippable increments to customers with minimal errors.

Why do you need agile project management?
Over the last decade, agile methodology in project management has gained popularity among project managers for running their projects efficiently and delivering value to customers. The concept of agile methodology is known to everyone, but why do you need to be agile in project management? Here are several reasons why you need agile methodology to operate projects successfully.
Agile methodology projects focus on incremental delivery of value to customers, enabling them to use the product sooner and provide constructive feedback for changes. This approach helps deliver an error-free and satisfying final product.
Continuous feedback from stakeholders allows the project team to iterate and adjust the product faster to align with requirements, resulting in less rework and lower costs.
Responding and adapting quickly to changing industry dynamics and customer needs results in achieving optimal customer satisfaction and a better position in the market among competitors.
Agile methodology emphasizes open communication with stakeholders and clients, promoting transparency and clarity for decision-making. This results in timely development and faster releases to the market.
Delivering in incremental cycles allows teams to detect and respond to potential risks quickly and make informed decisions at the early stages of the project, leading to fewer project failures.
Importance of agile project management
- Higher customer satisfaction - Every process of agile methodology in project management is tailored towards delivering value to the customer. Keeping customer feedback at the forefront of task initiatives ensures that they are satisfied at all times.
- High product quality - Agile methodology follows an iteration-based approach. Feedback from both customers and stakeholders is incorporated into succeeding work cycles. This helps teams eliminate mistakes, faults, and continuously deliver a better end product.
- Allows for change - Teams that follow an agile management structure are flexible and responsive towards change. Agile ceremonies, specifically daily scrums, let them assess their progress regularly and make changes depending on the various situational factors.
- No unpredictable delays - Work cycles in agile project management are purposely short in nature. Breaking down large chunks of work into micro-cycles allows for more precise planning, tracking, and resource estimation, greatly reducing the probability of unexpected bottlenecks.
- Team dynamic gets better - Agile project development teams succeed because of their transparency and collaborative efforts. All members regularly interact through various agile ceremonies and are always in the loop regarding the overall progress of any project.
Who can benefit from agile project management?
When we are making breakthroughs in science and technology every day, embracing change has become second nature. It's almost Darwinian to say that if you don't keep improving, you're going to become obsolete. We make plans and drop relationships with a single text. In a sense, aren't we all agile?
The agile project development approach, which started out as an experiment for software-practitioners, has insinuated itself into every industry as a productivity mantra. Marketing, advertising, event planning, publications, and even food distributors have used agile knowledge to turn their luck around. We could almost call it a New Age Movement.
The 5 phases of agile project management
Jim Highsmith, one of the original co-authors of the Agile Manifesto, introduced the five phases of agile project management process. These points draw parallels to the five phases of project management. The phases have been used to provide a descriptive (rather than prescriptive) way of adopting agile project management.

Envision
The envision phase is the foundation of agile project management. Here, the project vision, scope, and goals are defined. During this phase, stakeholders and the project team come together to establish high-level objectives, set milestones, and identify potential challenges. It is an important phase that sets the groundwork for the project and aligns the team and stakeholders around a shared vision for achieving a successful project.
Speculate
The speculate phase sets the direction to start work on the project in a systematic and planned manner. This phase involves translating and breaking down large-scale objectives into workable items, detailed planning, creating a roadmap, and outlining how to achieve project goals. In the agile approach to project management, teams utilize this phase to set flexible timelines to adapt to changes based on continuous feedback loops, prioritize work, set team-level milestones, and prepare for efficient project execution.
Explore
Once scope setting and planning are complete, the explore phase kicks off. This is where planning turns into execution. During this phase, the product starts taking shape through iterative cycles called sprints, involving a continuous series of developing, testing, and refining. The explore phase is the heart of agile project management, embracing flexibility and improvements based on feedback to steer the project towards its goals.
Adapt
The adapt phase emphasizes on agility through adapting, improving, and refining based on constructive feedback. In this phase, the team takes a step back to reflect on what went well and what didn't, brainstorming solutions to improve processes and team dynamics to ensure the project progresses in the right direction.
Close
This phase signifies the end of the agile project management process. Here, the team finalizes deliverables, ensures that everything about the project is properly documented, and confirms stakeholder satisfaction before formally closing the project. During the closing phase, the team thoroughly reviews the project from start to finish to identify areas for improvement, capture lessons, and celebrate achievements before the formal conclusion.
Agile vs Waterfall: Which is right for project management in today's scenario?
| Waterfall Project Management | Agile Project Management |
|---|
| Linear and sequential approach | Incremental and iterative approach |
| Focuses on project delivery | Focuses on customer satisfaction |
| Delivers project in one go | Project is split into sprints |
| Requirements are taken only at the start of the process | Requirements are expected to change and evolve |
| Avoids scope changes once development begins | Incorporates changes even late in the development |
| Strict project deadlines enforced by the project manager | Teams are encouraged to be self-organizing |
| Focused on executing the plan | Focused on delivering working software |
In today's scenario, there are a myriad of project varieties that are undertaken across domains and Agile and Waterfall represent two very distinct project management approaches.
Agile is iterative, flexible, collaborative which inculcates continuous feedback and constant adaptation. Agile thrives in environments of uncertainty, dynamism and frequent engagement from stakeholders. It empowers teams to self-organize and adjust to whatever situation they may be faced with.
Waterfall, in contrast, follows a liner and sequential order that is characterized by a clearly defined project scope, thorough upfront planning and fixed requirements till the end of the project. The Waterfall model functions on predictability, clear milestones and extensive documentation making it ideal for projects that require stringent compliance.
Ultimately, choosing between Agile and Waterfall is directly tied to the type of project they are aimed to address. Agile favors complexity, change and ongoing input whereas Waterfall is inclined towards structure, clarity and fixed outcomes.
Top 6 agile frameworks in project management
Agility is the umbrella term beneath which many frameworks have mushroomed over the years. It's a mindset, and a framework is a set of rules with which you can convert lofty principles into tangible practices that you can incorporate in your work.
There have been many frameworks over the years. Here are a few popular frameworks within the agile methodology.

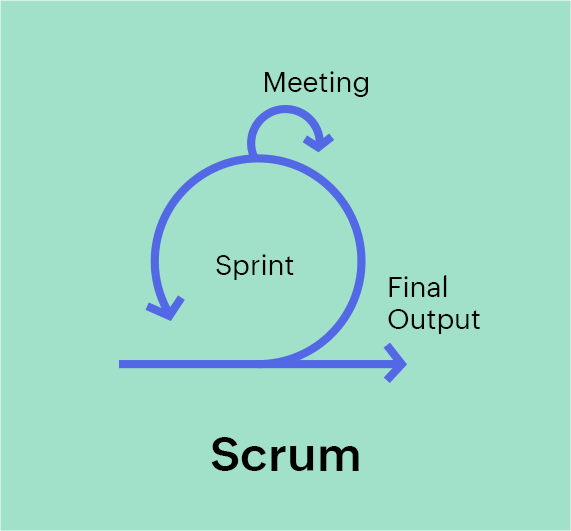
1. Scrum
Scrum is the quintessential agile project management framework. It is an iterative incremental approach to software development under agile project management and is also the most popular framework under the agile methodology. In Scrum, you split your work into chunks on which you work for set periods of time. These time boxes—called sprints— are tracked on a Scrum board and should result in a working piece of software. Scrum prescribes an inspect-and-adapt approach. So with each sprint, they adapt by incorporating lessons from previous sprints.
Scrum has 3 roles - Product Owner, Scrum Master and the development team. They each have distinct roles to play. The Scrum process starts with the "backlog" —a list of requirements—where each requirement is broken down into user stories and their corresponding tasks. These user stories are prioritized in order to plan the next sprint. There are several reports in Scrum that help a team measure the performance of a sprint - velocity, burnup, burndown, cumulative flow diagram. Scrum also emphasizes in face-to-face communication and small feedback loops within the team which is why meetings play an important role in the Scrum process.
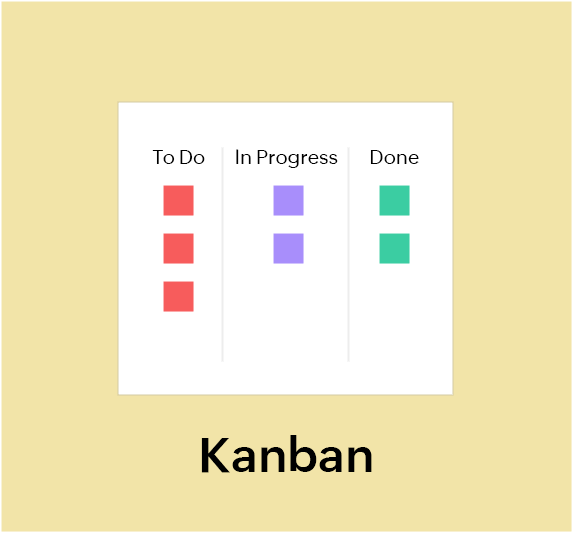
2. Kanban
Kanban is a method to visualize your workflow that lets you identify bottlenecks and increase productivity by limiting the amount of work in progress. It's based on the Japanese philosophy Kaizen, the idea that small continuous changes result in a substantial movement over time.
A basic Kanban board typically has three columns - "To do", "In progress", and "Done." Each work item is written on a Kanban card which also holds details like the description of the work item and the assignee. The Kanban cards are placed in their respective columns on the board. Each column has a work-in-progress limit which prevents the team from becoming overburdened and lets them focus on delivering quality work.
Kanban is a flow-based agile project management method which advocates continual delivery. Performance is usually measured by how long a work item takes to go from "To do" to "Done" on the board. This method focuses solely on preventing capacity overload and enabling quality and continuous delivery.
3. Extreme project management (XPM)
Extreme project management is an agile approach best suited for complex, fast-paced, and non-hierarchical projects with high uncertainty. It underscores constant adaptation and resilience to achieve desired outcomes. The XPM approach prioritizes flexibility, allowing frequent changes in timelines and strategies, and using trial-and-error to keep pace with evolving technologies and dynamic environments.
4. Feature driven development (FDD)
Feature-driven development, also known as FDD, is a methodology in the agile framework centered on providing timely updates and fully functional features to clients. Unlike Scrum, which is a delivery-focused approach, FDD is feature-driven, where fully functional features must be rolled out every 2–10 days, whereas a sprint cycle lasts for two weeks to a month. The feature-driven approach in agile project management values documentation and highly relies on it, while other methods conduct daily meetups as a source of communication for updates.
The FDD approach was devised by IT strategist Jeff De Luca in 1997 to manage a project for a bank in Singapore, which turned out to be a huge success, leading to widespread adoption of the FDD model.
This approach is designed around five crucial steps spanning the entire product lifecycle, focusing on large feature-specific projects:
- 1. Develop an overall model
- 2. Build a feature list
- 3. Plan by feature
- 4. Design by feature
- 5. Build by feature
5. Dynamic systems development method (DSDM)
The dynamic systems development method is an agile approach introduced in 1994 as an improvement to project management, replacing the rapid application development (RAD) approach. DSDM adheres to strict timelines and budgets, supported by ranking requirements from the highest level of importance to the lowest.
The DSDM approach includes the following five phases:
- 1. Feasibility study
- 2. Business study
- 3. Functional model iteration
- 4. Design and build
- 5. Implementation
6. Adaptive software development (ASD)
This agile project management methodology emphasizes extensive and rapid adaptability and responsiveness to changing requirements and environments, evolving products with little planning, and continuous learning experiences. ASD focuses on the quality of outcomes rather than the tasks performed to achieve them.
There are three phases in ASD reflecting unpredictability and continuous learning:
- 1. Speculate
- 2. Collaborate
- 3. Learn
Kanban vs Scrum: When to pick one?
"Kanban vs Scrum" is quite a popular debate within agile project management circles. While there are some key differences between the two, both are fundamentally based on agile principles like adapting to change, transparency and constant, consistent improvement.
Scrum is more prescriptive of the two with strict time boxes, ceremonies and artifacts. Kanban is favored by teams who deliver continuously and are working on optimizing their workflow. If you don't like either, there's a third option Scrumban, which combines the structure of Scrum and the flexibility of Kanban.
Each team operates differently. The framework you choose for your team depends on your work, your organizational culture and your team dynamic. That being said, the framework you choose will directly influence your team's productivity and job satisfaction. So choose wisely :)
4 Practical Steps to Implement agile in Project management
- Decide if agile is the right approach: Before implementing the agile methodology, it is crucial to determine if this approach is the right fit for your team and project. This decision can be based on multiple factors, such as the nature of the projects your team works on and the overall organizational culture.
- Select an agile framework: There is a plethora of agile frameworks and practices to choose from, serving different purposes and requirements. When selecting an appropriate agile project management framework, consider the character and size of your team and the project requirements to choose the approach that works best for your team.
- Plan your projects well: The next step towards an agile approach is to plan your projects meticulously. Planning is essential for clearly delineating the scope and objectives and preventing unexpected setbacks through setting up clear roadmaps and project backlogs.
- Measure success: Agile methodology emphasizes continuous improvement, so it is important to measure success to understand what went well and what did not to help teams perform better in upcoming projects. This can be achieved through regular retrospectives and sprint reviews.
What is agile project management in software development?
Agile project development (also called agile software development) is a project management approach that is now the go-to choice for software development. This approach values flexibility, responsiveness, and continuous improvement from start to finish of the software development process through active collaboration and adaptation to dynamic requirements. Agile software development advocates delivering fully functional fragments of the software in increments rather than a single large release and incorporates regular iterations based on feedback. You can learn more about this approach on our dedicated page about agile methodology.
Common challenges in implementing agile methodology in project management
Incorporating agile methodology in project management brings a lot of advantages, but its implementation isn't necessarily going to be a walk in the park. The primary challenges that organizations face in the implementation of agile project management methodology can be broadly attributed to cultural, procedural, and structural resistance. The most commonly observed challenges fall into the cultural category, especially for organizations who are transitioning from traditional methods. They often tend to find it hard to embrace agile methodology's iterative and decentralized work approach.
Even after adopting agile practices, there is a significant possibility of superficial or inappropriate adoption. For instance, an organization might be conducting regular stand-ups or sprints without fully understanding their purpose or objective. This could lead to ineffective or even incomplete results. Other miscellaneous challenges involve being able to find the right mix between flexibility and defined structure, tracking progress with multiple short work cycles, and not being able to comprehend the metrics associated with agile project development.
The best approach to prevent the possibility of even encountering these challenges is to have a strong understanding of the methodology itself and its functioning. It is paramount that this knowledge should be circulated uniformly across all participating members of the teams. Unlearning certain practices is also crucial as they may interfere with the agile way of working. Teams that focus on the "why" aspect instead of just the "how" find success with agile frameworks much easier. Lastly, a phased transition instead of going completely agile overnight will always yield more effective results.
Hybrid project management: Blending Traditional PM with Agile PM
Agile is undoubtedly the booming trend in today's project management era. However, the advantages of traditional project management cannot be denied. When weighing both project management frameworks, they have their own pros and cons, making it difficult to choose one methodology over another. That's why hybrid project management is the ideal solution, where strategic planning from the classic method is combined with the flexibility and iterative nature of agile to manage and achieve projects triumphantly.
How does an agile project management software help projects?
In today's competitive software development era, where quickly seizing the right opportunities and adapting to changing customer needs and market dynamics has become crucial for success, companies are shifting to agile project management methods. Every project team that aims to develop and deliver products in proper iterations and increments requires robust and efficient agile project management software to support and execute an agile project where design, development, and testing can happen simultaneously.
An agile project management software helps project teams by allowing them to:
- Create projects.
- Plan and prioritize project requirements.
- Execute sprints and track progress.
- Visualize progress and analyze performance, pitfalls, and potential risks.
- Support release plans for incremental delivery.
- Enable extensive communication with stakeholders and across teams to plan, execute, and deliver value to customers.
Going agile with Zoho Sprints
Agility is a concept, and an agile tool is the crucial catalyst that helps you convert your ambitious efforts into tangible results. You must decide what you want out of a tool before the evaluation process.
We kept all of that in mind as we developed Zoho Sprints, a lightweight, flexible tool that can be used equally well by teams large and small, industries IT and non-IT, and seasoned agilists as well as beginners.
Zoho Sprints ticks all the boxes when it comes to agile essentials with dedicated modules for backlog management, sprint planning, organizing epics, release management and so on. It functions as a scrum software as well as a kanban software so that you have the freedom to choose your approach based on your intricate preferences for each project you undertake. Beyond the basics, Zoho Sprints is also equipped with advanced features like a dedicated OKR tracking tool, budget management suite and a host of collaboration functions.
Change is the essence of agile and we've built Zoho Sprints in a way that it adapts to your processes and progress irrespective of what stage of growth you are in.
Get StartedFAQ
What is an agile project?
An agile project is a type of project that functions on principles of the agile approach, which emphasizes flexibility, adaptability and responsiveness. It is centered around continuous feedback loops and delivering value to the customer in short and frequent cycles.
Why choose the agile approach for project management?
The agile approach is the ideal solution for complex projects that have evolving or uncertain requirements requiring stakeholders to revise plans and priorities across the project cycle. This requirement perfectly aligns with the mechanics of the agile approach.
When is it best to use agile project management?
Agile project management is best suited for addressing the requirements for fast-paced environments with rapidly changing market demands. Sectors like software development, product development, marketing and IT are the most compatible with the agile style.
What is the difference between Agile methodology and Agile project management?
Agile methodology is the overall framework that describes how work should be done in a flexible and iterative approach by giving importance to adaptability and collaboration. Agile project management is the process of applying the principles of agile methodology to conduct a project.
What are the 4 core values of Agile project management?
The 4 core values of agile project management are:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools.
- Working software over comprehensive documentation.
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation.
- Responding to change over following a plan.
Can agile be used for non-software projects?
Yes it can. Although agile was originally incepted to tackle the challenges of software development projects, it also effectively supports several industries like marketing, human resources, product development, etc. that have evolved into a more fast-paced and dynamic setting. Agile helps here as well by breaking down big chunks of tasks into smaller, manageable portions that can be revisited as the conditions evolve.