Complete guide to filing GSTR 3B
What is GSTR 3B?
The GSTR-3B is a consolidated summary return of inward and outward supplies that the Government of India has introduced as a way to relax the requirements for businesses that have recently transitioned to GST.
Since a lot of small and medium businesses have been using manual accounting methods, filing returns within the July 2017 deadlines would be difficult for many of these businesses. Hence, from July 2017 to June 2018, tax payments will be based on a simple return called the GSTR-3B.
- If Form GSTR-1 is filed late (post the due date), the late fee will be auto-populated and collected in the next open return in Form GSTR-3B.
- From January 1, 2022, taxpayers will not be permitted to file Form GSTR-1 if they have not filed Form GSTR-3B in the preceding month.
When to file GSTR-3B?
Starting 1 January 2021, small taxpayers with aggregate turnover of less than 5 crores can file quarterly GSTR 3B. Tax liability will be auto populated from GSTR 3B to GSTR 1 while filing returns.
Prerequisites for filing GSTR 3B
- The GSTR-3B form should be submitted by any business that is liable to file the monthly returns GSTR-1, GSTR-2 and GSTR-3.
- The GSTR-3B form can be easily filed online through the GSTN portal. The tax payable can be paid through challans in banks or online payment.
- You either need an OTP from your registered phone to verify your return using an EVC (electronic verification code) or a digital signature certificate (of class 2 or higher). You can also file your GST returns using an Aadhar based e-sign.
How to file GSTR 3B?

On the GSTR-3B, you will have to provide your GSTIN and legal name, and complete other tax-related sub-sections such as:
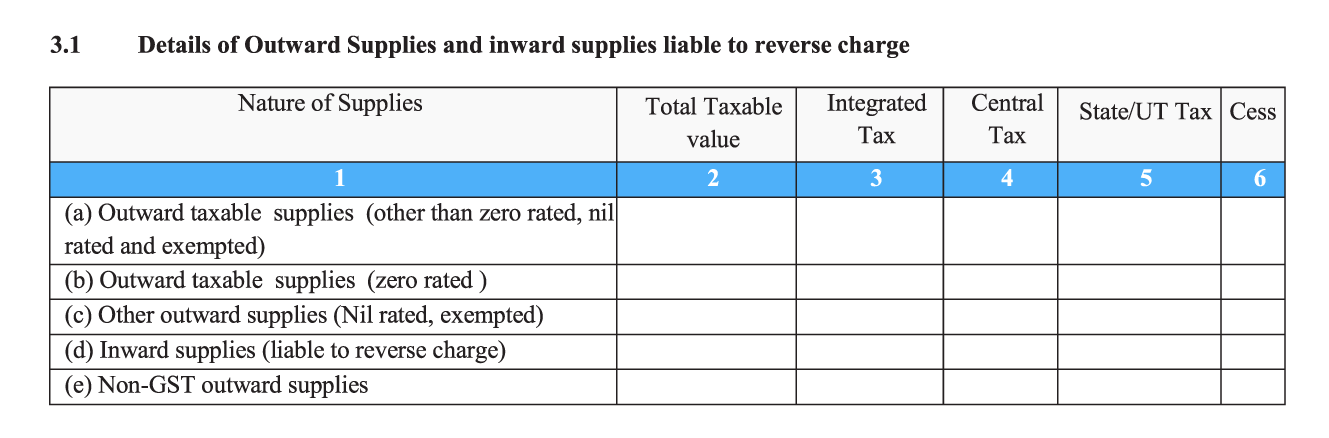
- 3.1. Details of your sales and purchases which are liable for reverse charge: In this section, you will have to enter the total taxable value (equal to the total value of items and services on invoices + debit notes - credit notes + advance tax received), and tax collected under different tax heads (IGST, CGST, SGST/UTGST, and Cess) for the following:
- Sales supplies (Zero rated supplies - includes items and services that are exported by you overseas, deemed exports or those sold to SEZ units or developers).
- Sales supplies (other than zero rated, nil rated and exempted - includes all regular taxable sale of items and services made by you).
- Other sales supplies (Nil rated and exempted supplies. It’s important to remember that nil-rated and exempted goods and/or services under GST are not the same. Nil-rated products are not taxed at the time of sale, but input tax credit can still be claimed for them. Exempted products are not taxed at the point of sale, and no input tax credit can be claimed for them.)
- Purchase supplies liable for reverse charge (purchase transactions where you are liable to pay the tax directly to the government on behalf of your supplier who may or may not be registered under GST).
- Non-GST sales supplies (for example, petrol)
- Cess is applicable to certain industries such as automobiles and tobacco. If your business is not involved in selling such goods, there’s no need to enter cess-related details.
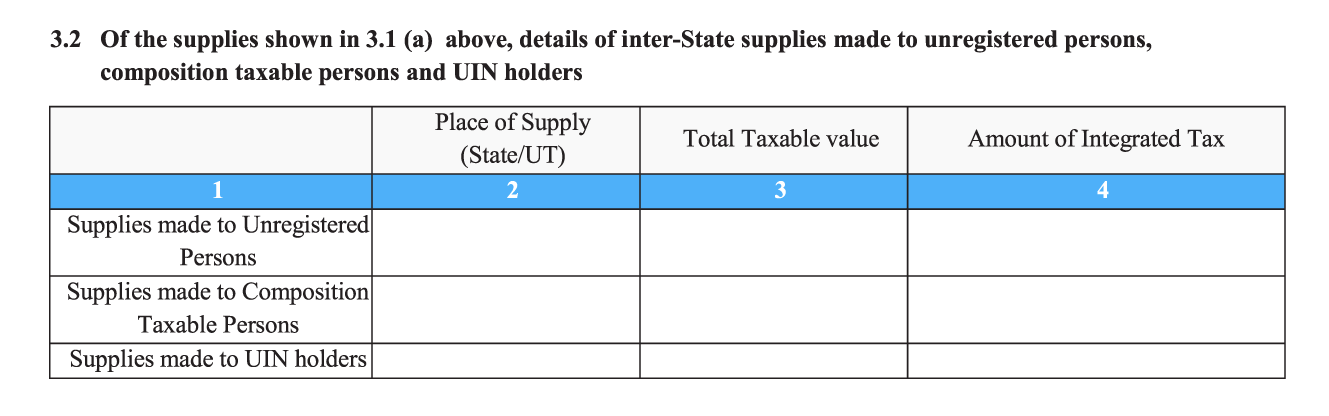
- 3.2. Details of inter-state sales made to unregistered buyers, buyers registered under the composition scheme, and UIN (Unique Identification Number) holders: In this section, you will have to fill in details regarding the place of supply (in simple terms, this is the location of the customer/the place where you deliver goods or services), total taxable value (amount on the invoice), and IGST collected for the following types of interstate sales made by you:
- Supplies made to unregistered people (includes unregistered businesses and end consumers).
- Supplies made to Composition Taxable people (registered businesses who have opted for the composition scheme).
- Supplies made to UIN holders
- Unique Identification Number (UIN) holders include the following:
- Any specialized agency related to the United Nations Organization.
- Consulates or embassies of foreign countries.
- Multilateral Financial Institutions or Organizations included under the United Nations Organizations Privileges and Immunities Act of 1947.
- Any person or group of people who have been designated by the Commissioner to receive a UIN.
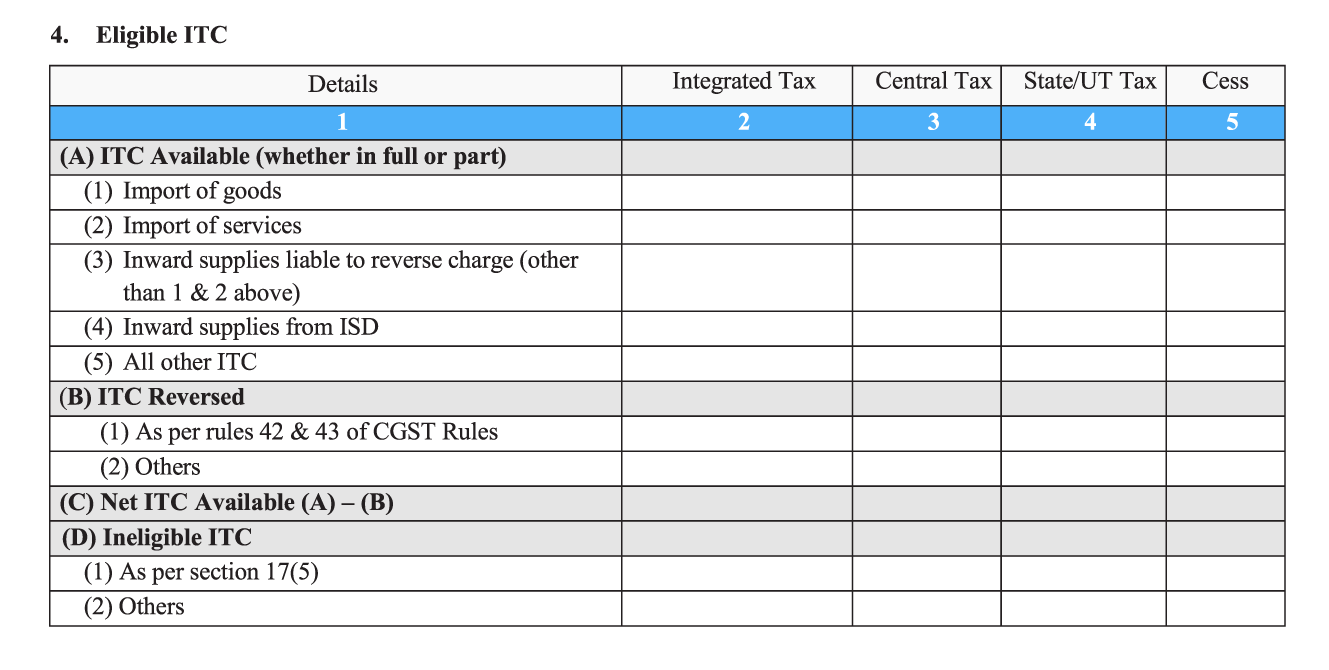
- 4. Eligible ITC (Input Tax Credit): Your final tax payment and credits will be calculated based on your income tax credit (ITC). In this section, you will have to enter details about the following:
- (A) ITC available (whether in full or part): Enter the tax amounts related to import of goods (1), import of services (2), inward supplies liable for reverse charge (3), inward supplies from Input Service Distributors (4), and all other ITC (5) that is not included under subsections (1) and (2) of section 4A.
- (B) ITC Reversed (per rules 42 and 43 of CGST rules): Under this you will have to furnish details of capital goods/services that have been utilised for non-business purposes. The ITC against such items and services will be made unavailable to you since legally, you can only claim ITC on taxable goods and services by selling them or for business purposes.
- (C) Net ITC available: Calculate this by subtracting the reversed ITC (B) from the available ITC (A).
- (D) Ineligible ITC (per section 17(5) and others): This includes blocked credits, which occur when certain services are involved. You are not allowed to claim ITC on transportation services (if they’re not for the purpose of supplying goods), food, health services, cab services for employees, and beauty services by default.
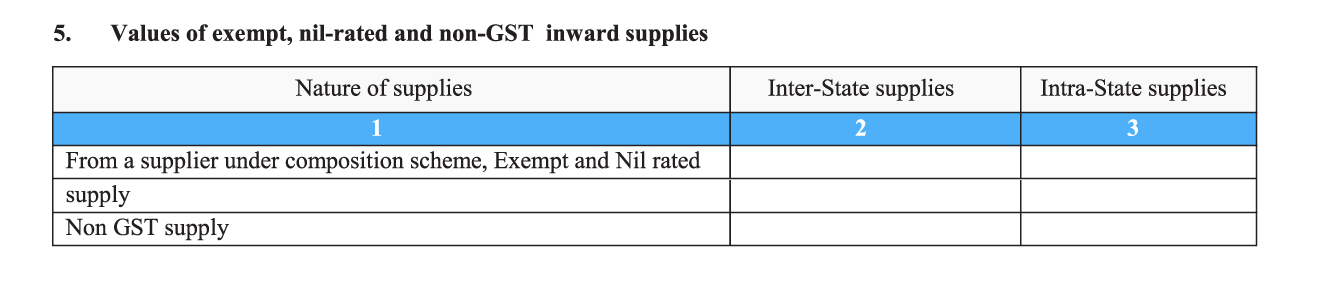
5. Values of exempt, nil-rated, and non-GST inward supplies: Under this sub-section, the taxpayer should enter taxation details for inter-state and intra-state purchases made. This includes supplies purchased from a supplier under the Composition Scheme, purchase of items and/or services that are either exempt from GST (they attract 0% GST but you as a taxpayer cannot get a refund of tax paid on inputs), nil-rated (attract 0% GST by default but allows you to claim refunds of tax paid on inputs used to effect them) or non-GST supplies (items that do not come under the purview of GST and may instead attract state VAT under the old system).
5.1. Interest and Late fee payable: This may apply to only those businesses who have some additional tax liabilities imposed on them (this may arise whenever they fail to comply with one or more GST regulations). If this applies to you, then you are to declare the aggregate amount of interest and/or late fee applicable on taxable supplies that may or may not attract tax on reverse charge under different tax heads (IGST, CGST, SGST/UTGST and Cess).
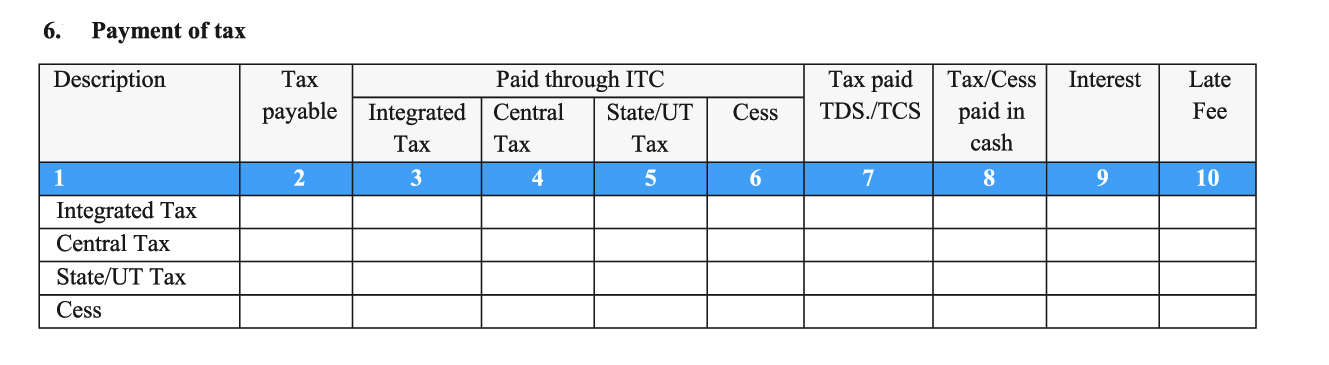
- 6. Payment of tax: You have to pay the GST you owe to the government before filling up this section since, it captures the overall tax amounts paid for CGST, SGST, IGST, and cess. Include the overall tax payable, tax paid through ITC (by offsetting the amount paid on inputs as tax), tax paid with respect to TDS/TCS credits, and tax/cess that was paid in cash (this also includes those amounts paid as interest and late fee).
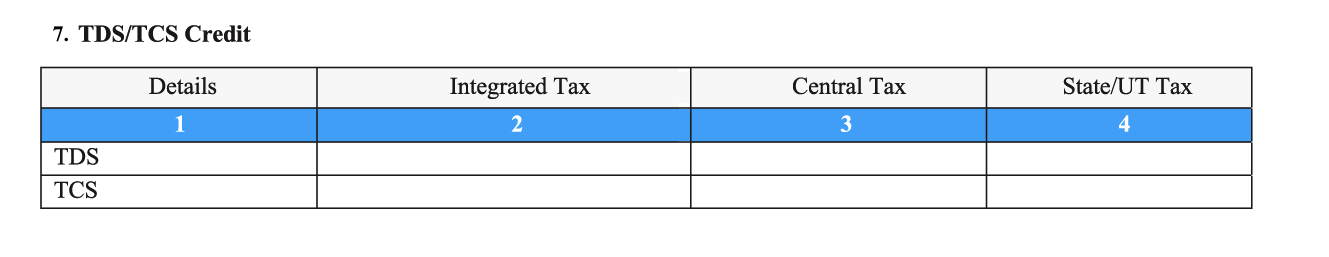
- 7. TDS/TCS credit: Whenever a customer or an e-commerce deducts or collects tax at source, then you receive credit against it. If you have accumulated such credits during this month, (also known as TDS/TCS credits) they are captured under this section under different tax heads (IGST, CGST, SGST/UTGST).
After filling in all these details, the GSTR-3B form can be submitted after being signed by the authorized taxpayer.

