Complete guide to filing GSTR 1
GSTR-1 is a sales return that is required to be filed by every GST registered person. Tax payers are to enter details relevant to their sales & outward supplies in the GSTR 1 sales return.
- If Form GSTR-1 is filed late (post the due date), the late fee will be auto-populated and collected in the next open return in Form GSTR-3B.
- From January 1, 2022, taxpayers will not be permitted to file Form GSTR-1 if they have not filed Form GSTR-3B in the preceding month.
- Availing ITC for invoices and debit notes apply only in cases where details of these invoices / debit notes are provided in Form GSTR-1 / IFF and communicated to the registered person in Form GSTR-2B. This is applicable only after section 16(2) (aa) of CGST Act, 2017 is notified.
- What is GSTR 1?
- GSTR-1 due date
- Prerequisites for filing GSTR-1
- How to file GSTR 1
- GSTR-1 for different businesses
- Making changes to sales data after filing GSTR-1
What is GSTR 1?
The Goods and Services Tax Return 1 is a document that each registered tax payer needs to file every month/quarter.
- It must contain the details of all sales and supply of goods and services made by the tax payer during the tax period.
- However this return is not applicable to composition vendors, non resident foreign taxpayers and those with an Unique Identification Number.
GSTR-1 due date
Starting 1 January 2021, small taxpayers with aggregate turnover of less than 5 crores can file quarterly GSTR 1 and GSTR 3B. The due date for filing the GSTR 1 return will be the 13th of the consecutive month in the succeeding quarter. However, the taxpayers can continue to submit invoices every month.
Prerequisites for filing GSTR-1
- You must be a registered tax payer under the GST with a 15-digit PAN-based GSTIN.
- You need to keep detailed invoices with unique serial numbers for all of your transactions, including intra-state as well as inter-state transactions, and business-to-business (B to B) as well as retail (B to C) sales. This also includes transactions associated with exempted and non-GST supplies, and stock transfers between your business locations in different states.
- You either need an OTP from your registered phone to verify your return using an EVC (electronic verification code) or a digital signature certificate (of class 2 or higher). You can also file your GST returns using an Aadhar based e-sign.
How to file GSTR 1
The GSTR 1 format consists of a variety of information such as the taxpayer’s sales and outward supplies. Let’s take a look at each section in detail.
The first section asks for the year and the tax period for which the GSTR-1 is filed. The following sections ask for the tax details from that period.
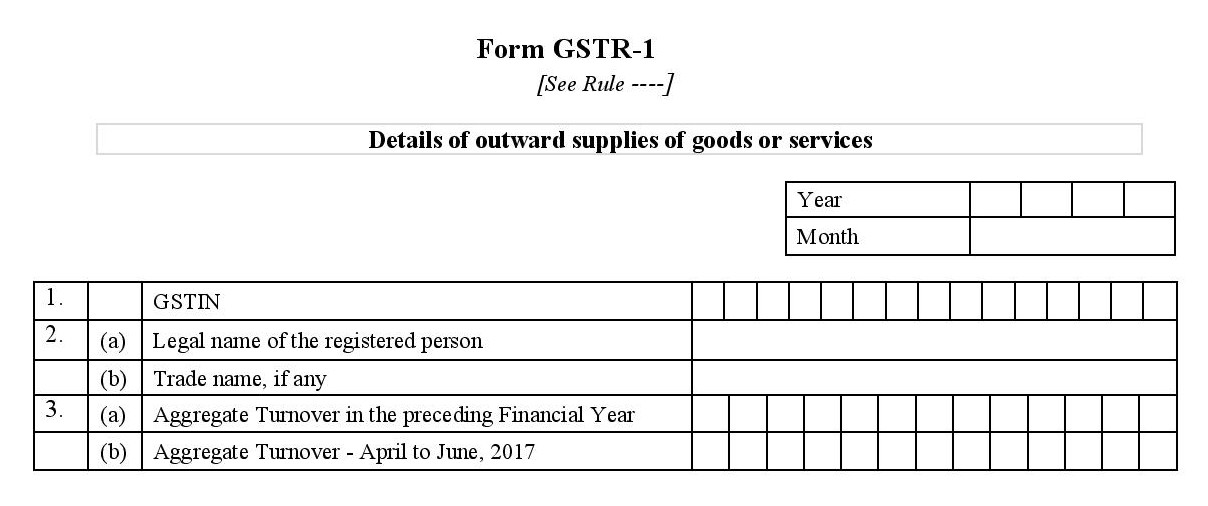
- 1. GSTIN: (your unique PAN-based 15-digit Goods and Services Taxpayer Identification Number).
- 2. Name of the Taxpayer:
- Registered person’s legal name
- Trade name (if any)
- 3. Turnover of the Taxpayer:
- Aggregate turnover in the preceding financial year: the total value of sales and supplies you made in 2016-2017 minus taxes. This is the only year you will need to provide this — in the future, it will be auto calculated and auto populated.
- Aggregate turnover - April to June, 2017: the value of sales and supplies you made between the start of the fiscal year and the GST rollout.
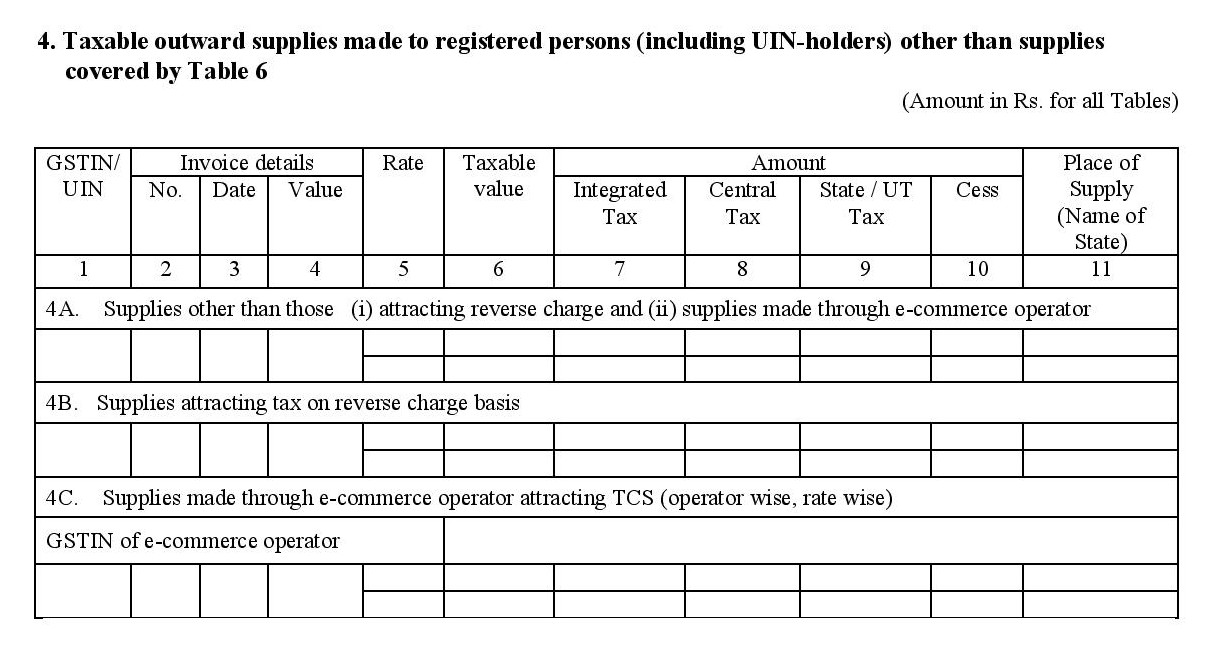
- 4. Taxable outward supplies made to registered persons (including UIN holders) excluding the contents of table 6:
- Invoice-wise details of all taxable B to B supplies you made for this tax period, excluding sales involving reverse charge and sales made through an e-commerce portal. Provide the breakdown of CGST, SGST, and IGST for each.
- All B to B sales made this tax period that attract reverse charge. (e.g., services offered by a Goods Transport Agency or taxi services through an e-commerce aggregator)
- Supplies made online through an e-commerce channel (such as Amazon or Flipkart). The data here has to be categorised by GSTIN(s) of the e-commerce operator/channel(s) involved.
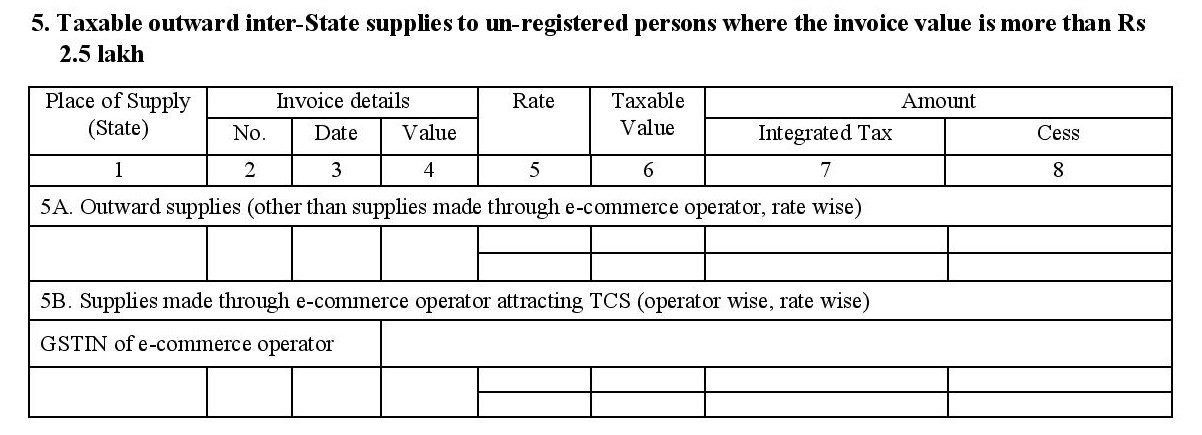
- 5. Taxable outward inter-state supplies to an unregistered consumer where the invoice value is more than Rs. 2.5 lakh: This section is dedicated towards the sales made to large consumers (where the invoice amount is above 2.5 lakh rupees) or unregistered businesses.
- Invoice details of B to C supplies (made to end consumers) and B to B supplies (made to unregistered businesses) you have made across different states, excluding e-commerce sales goes here.
- Invoice details of interstate B to C supplies made online including place of supply, taxable value, GSTIN of the e-commerce operators involved, etc., go here.
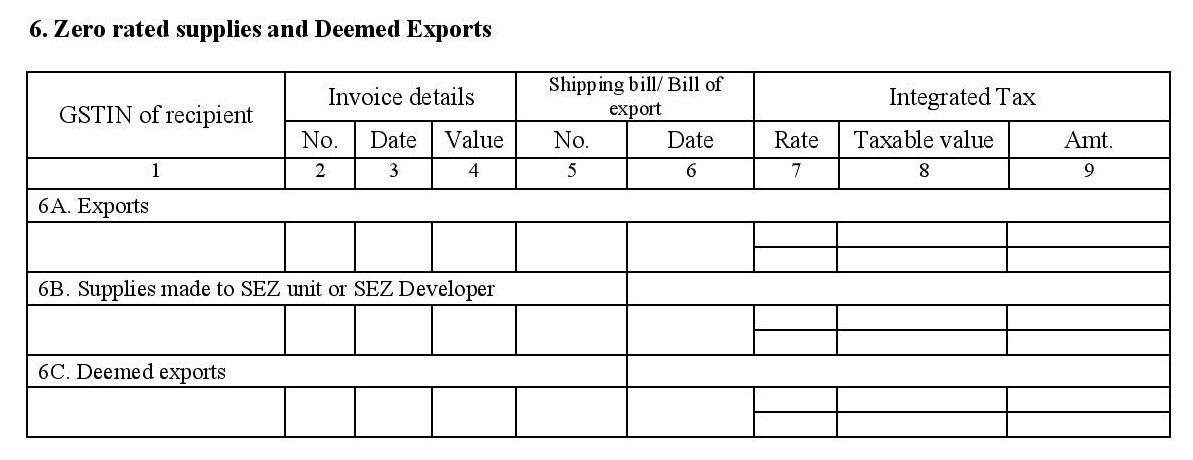
- 6. Zero-rated supplies and deemed exports:
- All exports you made during the tax period. Provide invoice details, shipping bills and details of any taxes involved.
- Supplies made to customers located within a Special Economic Zone (SEZ unit or SEZ Developers).
- Deemed exports you have made during the tax period. According to section 8.1, chapter 8 of foreign trade policy 2015-2020, These are transactions that are treated as exports even though the goods aren’t leaving the country yet. You may be supplying goods to Export Oriented Units, software or hardware technology parks, or government-funded projects, and getting paid in either INR or free foreign exchange (equivalent of INR in the currency of the customer for the invoice date).
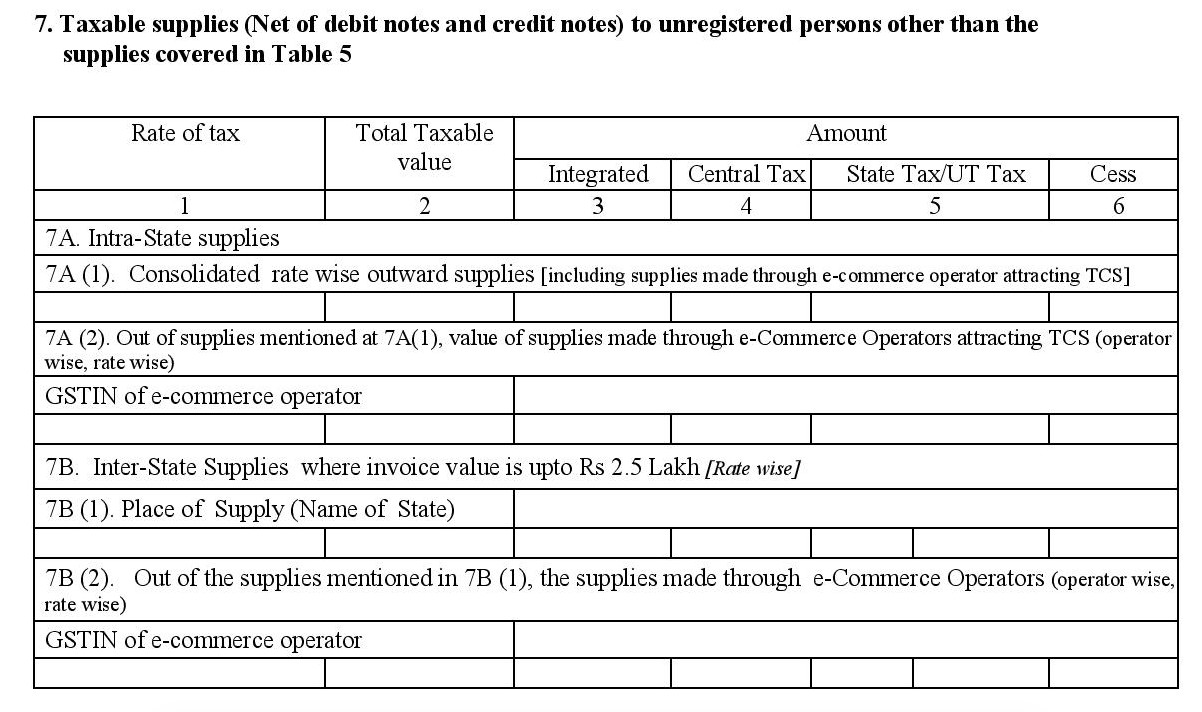
- 7. Taxable supplies (net of debit notes and credit notes) to unregistered persons, other than supplies covered under Table 5: This table captures a rate-wise summary of sales and supplies made for the tax period including taxable value and the tax collected under various heads.
- Intrastate supplies
- Consolidated details of B to C sales (both online and offline).
- Online B to C sales. Provide the GSTIN of the e-commerce operator(s) involved.
- Interstate supplies where the invoice amount is less than Rs. 2.5 lakh
- Details of B to C interstate supplies along with the place of supply.
- Details of B to C interstate sales made online. Provide the e-commerce operator’s GSTIN.
- Intrastate supplies
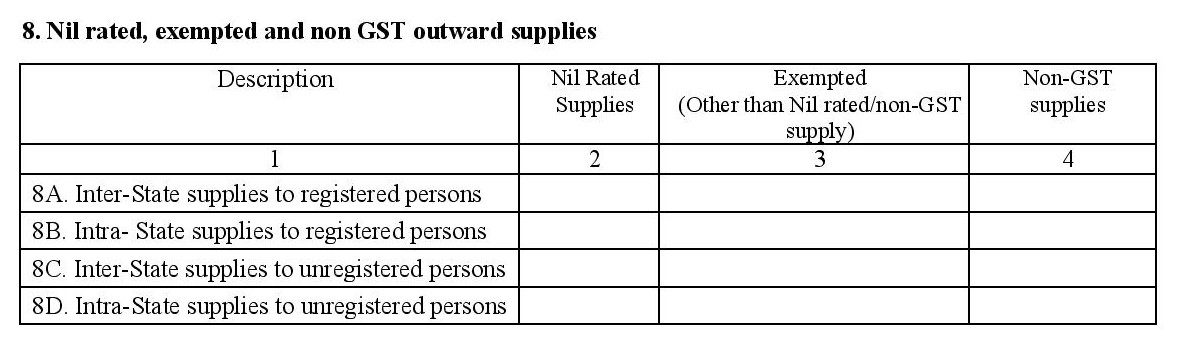
- 8. Nil rated, exempt, and non-GST outward supplies: Capture the sales summary of items and/or services that are nil rated (0% GST but allow you to claim ITC on tax paid for inputs), exempt (those which do not attract GST but do not allow you to claim ITC on tax paid for inputs) and non-GST supplies (those which are outside the purview of GST and may attract other taxes like state VAT).
- Interstate supplies made to registered persons: B to B sales made to GST registered businesses in other states
- Intrastate supplies made to registered persons: B to B sales made locally (to GST registered businesses located in the same state).
- Interstate supplies made to consumers and unregistered persons: B to C sales made to customers and unregistered businesses located in other states.
- Intrastate supplies made to consumers and unregistered persons: B to C sales made locally (Includes end consumers and unregistered businesses).
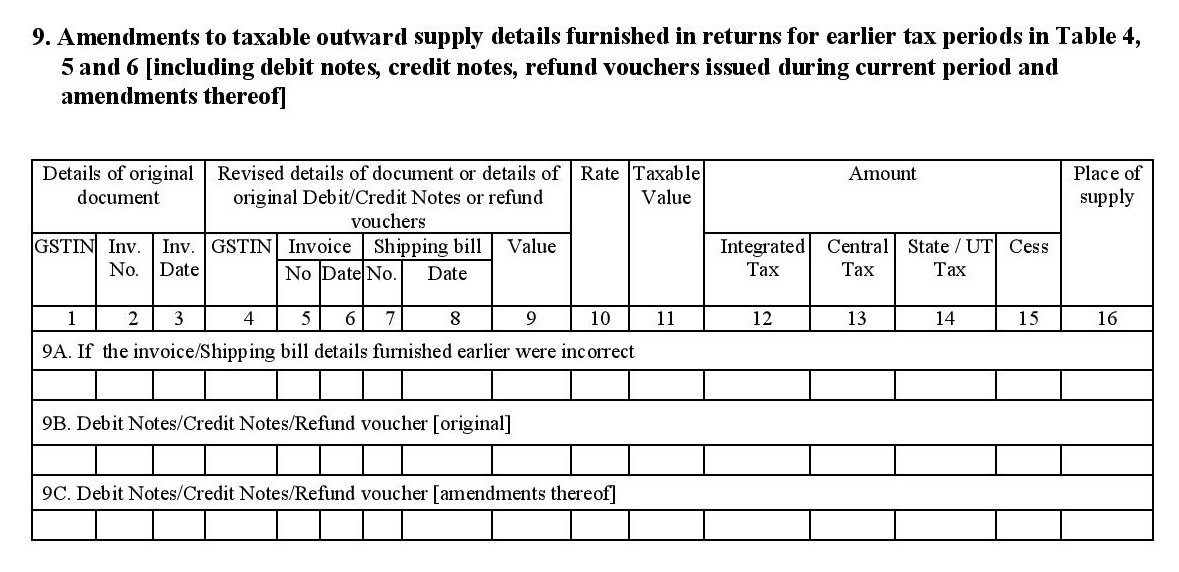
- 9. Amendments to taxable outward supply details furnished in returns for earlier tax periods in table 4, 5 and 6 (including current and amended debit notes, credit notes, and refund vouchers): Using this section, you can make changes or corrections to the sales records that you have submitted during the previous tax periods.
- Details of incorrect invoices and shipping bills submitted on previous returns, along with the corrections.
- Original debit notes, credit notes and refund vouchers created during the current tax period.
- Changes made to the debit notes, credit notes and refund vouchers filed during earlier tax periods. (Here, you are also required to furnish the details of the original document that is being revised including GSTIN of the customer, document number, date, etc.).
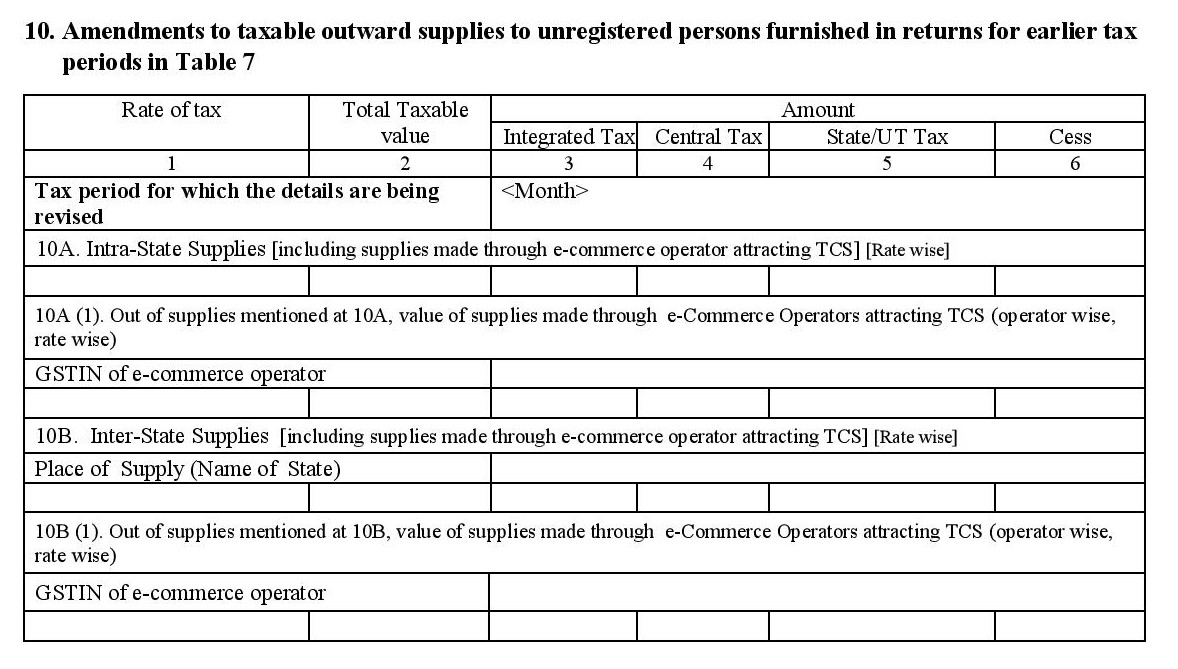
- 10. Amendments to taxable outward supplies to unregistered persons furnished on returns for earlier tax periods:
- Modifications made to intra-state sales (local/within your state) and supplies which were made either online or offline during previous tax periods including the GSTINs of the parties involved are captured here.
- Modifications and corrections made to inter-state sales and supplies that were made either online or offline during previous tax periods including the GSTINs of the parties involved are captured here.
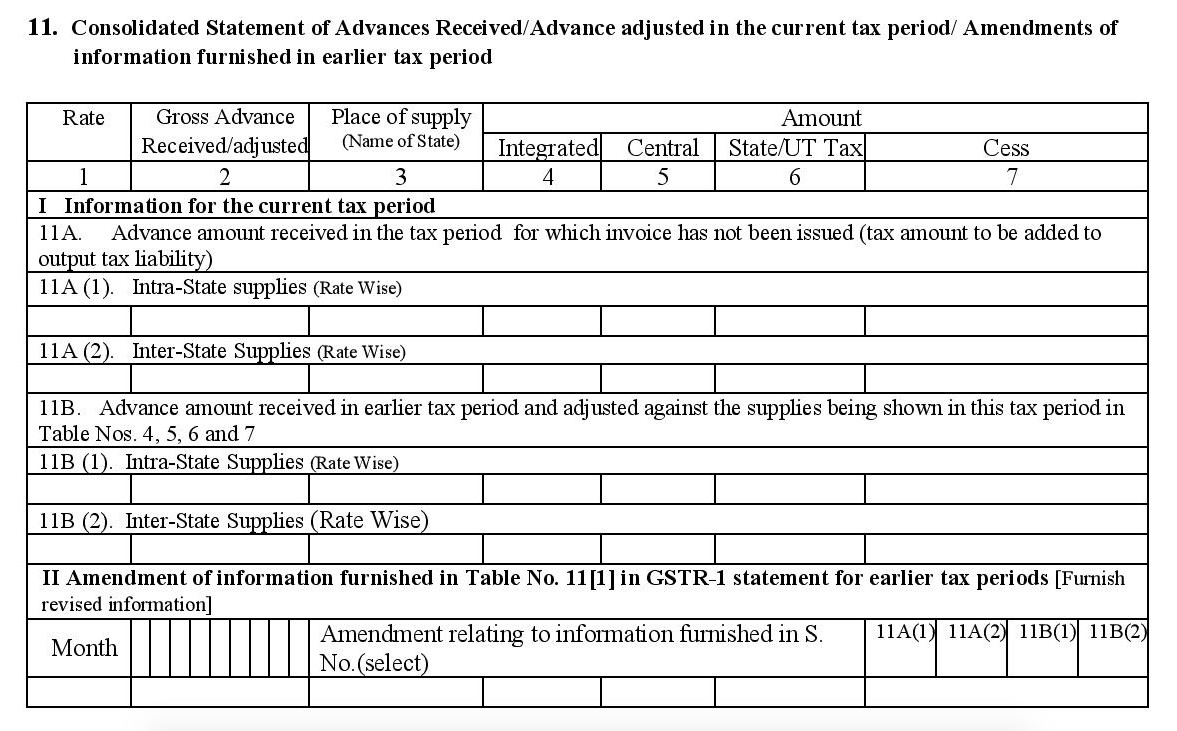
- 11. Consolidated Statement of Advances Received or adjusted in the current tax period, plus amendments from earlier tax periods
- a. Advance amounts you received during this tax period which have yet to be invoiced for (this includes both interstate and intrastate transactions).
- b. Advance amounts you received in earlier tax periods and adjusted against the supplies being made in this tax period under table 4, 5, 6, and 7.
- c. Any updates or changes made to the details under subsection 11A of earlier tax returns.
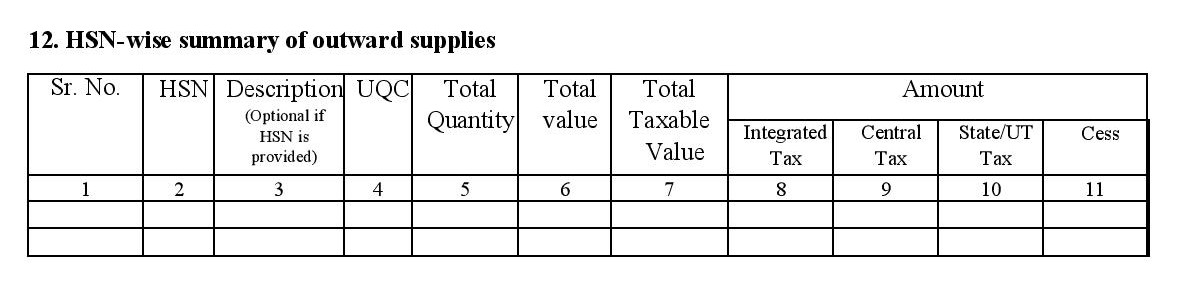
- 12. HSN-wise summary of outward supplies: Under this section, you are to provide a HSN wise summary of the items sold by you including total quantity sold, taxable value under each tax heading, and Unit Quantity Codes (for exports or imports).
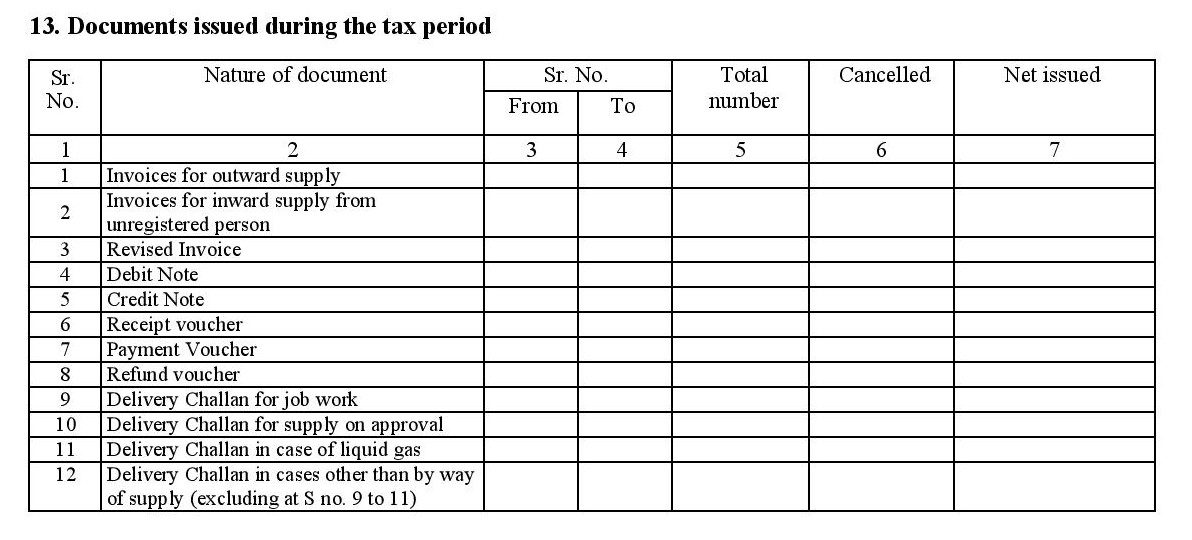
- 13. Documents issued during the tax period:
- Invoices for outward suppy: Sales invoices/the bills you give to your customers whenever you sell something along with their unique serial number, customer details, status of the invoice and the invoice count for the tax period.
- Invoices for inward supply from unregistered persons: They are purchase invoices under reverse charge. In simple terms they are bills given by unregistered vendors for which you pay the tax directly to the government.
- Revised invoices: Past invoices for which you have made corrections or modifications.
- Debit notes: Demand documents issued by you to your customers against any extra charges that may arise after the supply has been made (like overheads above projected cost on the invoice or for any mismatches or alterations after the sale).
- Credit notes: This includes refunds and post sale concessions given to customers.
- Receipt vouchers: A document issued to you by your customers whenever you send out goods along with a delivery challan but without the invoice.
- Payment vouchers: A document issued by you to your customers whenever they make payments against your invoices.
- Refund vouchers: A document with a unique serial number containing the details of a refund made to a person such as thew GSTIN of parties involved, goods or services for which the refund was made, amount refunded, date of refund, etc.
- Delivery challans: Documents that record the despatch of goods from your warehouse to another person or location. These are issued for various cases including job work, supply of liquid gas, supply on approval, etc. Based on the reasons of supply, they are captured under 4 different subsections of section 13.

At the end of the document, there is a declaration of truth that needs to be signed by the authorised signatory of your company.
Note: If you are using a GST compliant accounting and tax filing software (like Zoho Books), then the GSTR-1 will be auto-generated based on the transactions you record within the software. You can then push, reconcile and file this return directly into the GSTN.
GSTR-1 for different businesses
There are 13 tables and sections under GSTR 1. While each one is meant to capture a particular aspect of sales and outward supplies made under GST, not all of them are mandatory for every business (except for tables 1, 2, 3, 12 and 13 which are mandatory for all businesses). Hence, we have come up with a list of applicable GSTR 1 fields for a few business models. There are 3 things under GST that dictate the type of information you need to file within GSTR-1:
Your customer segment{#customer-segment}
- This is broadly classified into B to B and B to C.
- If you are a wholesaler or a manufacturer then your customer base will be full of businesses (B to B). In such a case, you will need to capture the details (at invoice level) of all your B to B sales under section 4A of GSTR-1. Any debit notes/credit notes that you send to them during this tax period needs to be captured under table 9.
- If you are a Goods Transport Agency or a supplier of goods or services mentioned under section 9 of the CGST law, then the supplies you make will attract GST under reverse charge (where in the customer is required to pay the GST directly to the government on your behalf). In this case, section 4B will apply to you.
- If you sell goods and/or services across multiple states to end consumers as well as unregistered business, then table 5 will apply to you. Table 5 also captures details of sales made to unregistered persons where the invoice amount is greater than 2.5 lakh rupees.
- If you are purely selling goods and/or services only to end consumers, then you may skip tables 4, 5, and 6 and directly head to table 7 since it captures invoice level details of sales made to end consumers including inter-state supplies and online sales made. If you are selling goods online through an e-commerce operator (like Flipkart, Amazon, etc.,) then you are also required to categorise your online sales based on the operator (along with their GSTIN).
- If you are an exporter of goods, then pay more attention to table 6 (especially 6A) since most of the supplies that you will be making to overseas will be zero rated. Here you are required to give the details of your shipping bills.
- Those of you who sell goods and/or services to customers located in a Special Economic Zone or make a deemed export within our country, sections 6B and 6C will apply to you.
The nature of supplies you make
Under the GST regime you can make 5 kinds of supplies - Taxable supplies/GST supplies, Nil rated supplies, Zero rated supplies, Exempt supplies and Non-GST supplies. You can learn more about each kind of supply here.
- Tables 4, 5 and 7 deal with Taxable supplies made within India under GST.
- Table 6 is dedicated to Zero rated supplies. These are items and/or services which are either exported out of the country, sold to a SEZ unit or developer or considered as a deemed export (whenever they are sold to an export oriented unit or whenever the goods do not leave the country while the invoice may be sent to an overseas customer).
- Table 8 is meant for capturing your nil rated, exempt and non-GST supplies made during a particular tax period. This includes the sales made within your home state as well as across other states.
Mode of supply
The two common modes of supplying goods and/or services are direct supplies and online supplies (those made through an e-commerce operator like Flipkart or Shopclues).
- Most sections under table 4 to table 11 handle direct supplies made by you (where the sale or supply was made through conventional means).
- Supply of goods and/or services made online through an e-commerce marketplace are captured under sections 4C, 5B, 7A(2), 7B(2), 10A(1) and 10B(1). On top of capturing the GSTINs of registered customers (if any), you are also required to capture the GSTIN of the e-commerce operator through which you made those supplies.
General Notes
While this may not apply for your July return (since it will be the very first GSTR-1 that you will file), from the next GSTR-1, you can make amendments (or legal modifications) to the data filed by you previously using tables 9 and 10.
- While table 9 is predominantly meant for your B to B transactions, it also captures the details of debit notes and credit notes issued by you to your customers for a particular tax period.
- Table 10 is essentially meant for your making corrections to sales documents for the sales made to your unregistered customer base during a particular month (under the GST regime).

