- HOME
- Know Your Tech
- Application governance: Types and best practices for 2026
Application governance: Types and best practices for 2026
- Last Updated : January 4, 2026
- 499 Views
- 10 Min Read
Are you struggling to manage the growing number of applications across multiple departments in your business? It’s a complex task that requires more than just oversight. We understand the challenge.
Highlights
- A structured governance framework is essential for managing applications, controlling costs, and ensuring compliance as your business scales.
- Proper governance helps business teams gain autonomy over app usage while maintaining secure access through clear policies.
- Automation drives consistency by simplifying processes like access reviews, audits, and compliance checks.
- Tracking metrics such as app usage, compliance conflicts, and cost ensures continuous improvement in governance effectiveness.
Without a solid governance framework, businesses face increasing IT costs, security vulnerabilities, and challenges in meeting compliance standards. Application governance ensures alignment across systems, covering access, ownership, and usage.
This blog post will walk you through the key aspects of application governance. You’ll discover why it’s crucial and how to implement it effectively to protect your business.
What does application governance mean today?
Application governance establishes policies and controls for managing applications throughout their lifecycle. It covers how apps are selected or developed, who can access them, how they're secured, and when they should be removed. The goal is to align your application portfolio with business objectives while managing security risks and compliance requirements.
Recent analysis reveals significant gaps in current approaches. Data shows that nearly 60% of organizations will fall short of their AI initiative goals by 2027 due to inconsistent data governance. This highlights how much disconnected governance influences real business impact.
Effective governance balances control with flexibility. Teams need the right tools to do their work, but organizations also need visibility into application usage, clear ownership, and automated policy enforcement. Modern governance focuses on enabling productivity while maintaining security and compliance standards across your entire application ecosystem.
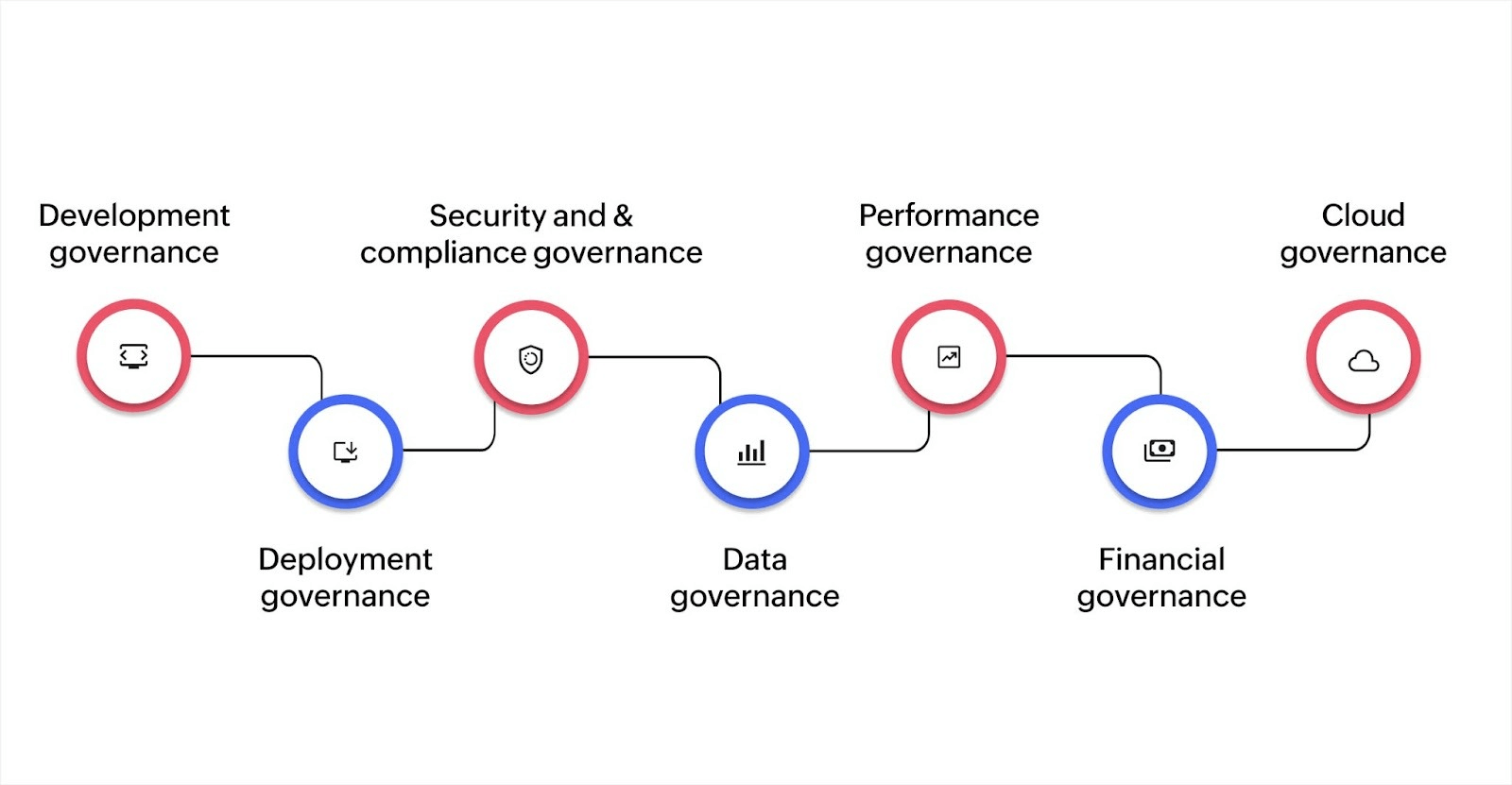
7 types of application governance
Different aspects of your application environment require specific governance approaches. Here's how the common types compare.
| Governance type | Primary focus | Key activities |
| Development | Code quality and security | Secure coding, testing, version control |
| Deployment | Release management | Change approvals, rollback procedures, testing |
| Security and compliance | Access and regulations | User permissions, audit trails, regulatory adherence |
| Data | Information handling | Classification, integrity, usage standards |
| Performance | Application health | Uptime monitoring, SLA tracking, resource optimization |
| Financial | Cost management | Budget tracking, ROI evaluation, resource allocation |
| Cloud | Cloud operations | Multi-cloud policies, security, service agreements |
Now let’s take a detailed look at the different types of application governance:
1. Development governance
This maintains code quality and security throughout the software development process. Secure coding practices prevent vulnerabilities before they reach production. Regular testing identifies issues early when they're less expensive to fix. Version control provides clear records of changes and enables quick rollbacks when problems occur.
2. Deployment governance
The deployment governance manages how changes move from development to production environments. Structured change approval processes ensure proper review before releases. Deployment governance reduces risk while maintaining predictable release schedules. Well-defined workflows let teams ship updates confidently without compromising stability.
3. Security and and compliance governance
This protects sensitive data and ensures regulatory adherence. Access management implements least-privilege principles so users can access only what their role requires. Regular compliance audits verify that you're meeting industry regulations and legal requirements. Strong security governance reduces breach risks while preparing you for regulatory reviews.
4. Data governance
Data governance establishes standards for handling information within your applications. When you classify data properly, sensitive information receives appropriate protection based on its importance. You can maintain reliable data for business decisions through quality standards. Usage policies prevent mishandling while teams still get access to the data they need for their work.
5. Performance governance
This helps organizations evaluate whether applications deliver expected value by tracking availability, response times, and adherence to service-level commitments. Monitoring application health identifies potential issues before users experience problems. Performance governance ensures that your applications support business operations reliably without unexpected downtime or degraded experiences.
6. Financial governance
The financial governance tracks costs associated with application usage and cloud resources. Regular reviews identify underutilized applications that waste budget. Financial governance helps you evaluate whether investments in applications generate appropriate business value. You avoid unnecessary expenses by managing resource consumption actively.
7. Cloud governance
This addresses the specific challenges of managing cloud-based applications and services. Clear policies govern how teams use cloud resources across SaaS, IaaS, and multi-cloud environments. Security controls protect data in cloud systems while compliance monitoring ensures adherence to cloud service agreements. Effective cloud governance lets you scale operations.
Importance of application governance

Strong governance balances security, compliance, and efficiency without stifling innovation. Let’s explore how an effective governance framework drives real value for businesses.
Prevents access sprawl
One of the main challenges in managing a growing number of applications is the uncontrolled access sprawl. When employees or departments are allowed to request or add apps freely and without oversight, it leads to increased risks.
Governance frameworks help prevent this by managing access. Organizations can limit unnecessary or unauthorized access, protecting sensitive data and systems from internal threats.
Speeds up audits
Regulatory compliance is becoming increasingly complex, with businesses required to adhere to various industry standards and legal frameworks. With governance policies in place, companies can quickly generate reports and evidence for audits.
Gives business users control over their tools
While IT teams have a significant role in managing apps, business users need to make decisions about the tools they use. Proper governance frameworks provide business teams with the autonomy to request, utilize, and manage applications while ensuring security.
Most modern low-code platforms support this approach by giving business users direct access to build tools while keeping IT controls in place. Teams can respond to needs quickly without waiting weeks for custom development. Security policies remain enforced through the platform's built-in governance features.
Cuts app spend by removing underused tools
One of the most significant opportunities for cost savings lies in removing underutilized applications. Application governance frameworks help identify tools that are no longer necessary or are being underutilized.
Regular reviews and audits of application usage ensure that every tool in the portfolio serves a clear purpose.
Establishes accountability
A well-structured governance framework establishes clear ownership of each application within the organization. This reduces reliance on IT teams for routine tasks like approvals or access requests.
Enables consistent rules across environments
Application governance ensures that rules and policies are enforced uniformly across all systems, reducing the risk of errors or misconfigurations. It provides the necessary structure to maintain control.
If you want governance that actually works in fast-moving environments, it starts with a few key moves that the most secure and scalable teams get right.
Best practices to implement application governance
Organizations that succeed with governance treat it as an ongoing practice rather than a one-time project. Here's how to implement application governance that actually works.
Assign clear application owners
Designate specific owners for each application from relevant business units. Owners must understand how their teams use the application and make informed decisions about access, renewals, and changes. This creates accountability while reducing the burden on central IT teams to manage every application decision.
Set up access controls with self-service options
Allow teams to request application access through self-service portals. Build in policy-based approvals so requests route to appropriate managers automatically. This speeds up access provisioning while maintaining security standards. Users get the tools they need faster, and IT teams handle exceptions rather than routine requests.
Enforce regular access reviews
Schedule periodic reviews where managers verify that their team members still need current access levels. Automated reminders ensure that reviews happen consistently. This practice identifies access that should be removed when people change roles or leave the organization. Regular recertification keeps permissions aligned with actual responsibilities.
Track meaningful metrics
Track metrics that actually help you improve governance. Application usage rates show which tools your teams use regularly and which ones remain unused. Request volumes and approval times tell you where access processes create delays. Compliance data reveals which policies cause friction in day-to-day work. When you review these metrics regularly, you can spot problems early and adjust your approach before small issues become bigger ones.
Integrate governance into development processes
Build governance into your software development lifecycle from the start. Include security and access controls as requirements during planning phases. Run automated policy checks as part of deployment pipelines. Early integration prevents governance from becoming a final gate that delays releases.
Start with critical applications first
Begin governance with applications that carry the highest security risks or compliance requirements. Success with mission-critical systems builds confidence and proves value. Expand governance gradually to less critical applications once processes work smoothly. This phased approach prevents overwhelming your teams.
Common mistakes that break governance programs
Over-engineering, lack of communication, and viewing governance as just an IT responsibility can undermine the success of the program. Here are some common mistakes to avoid.
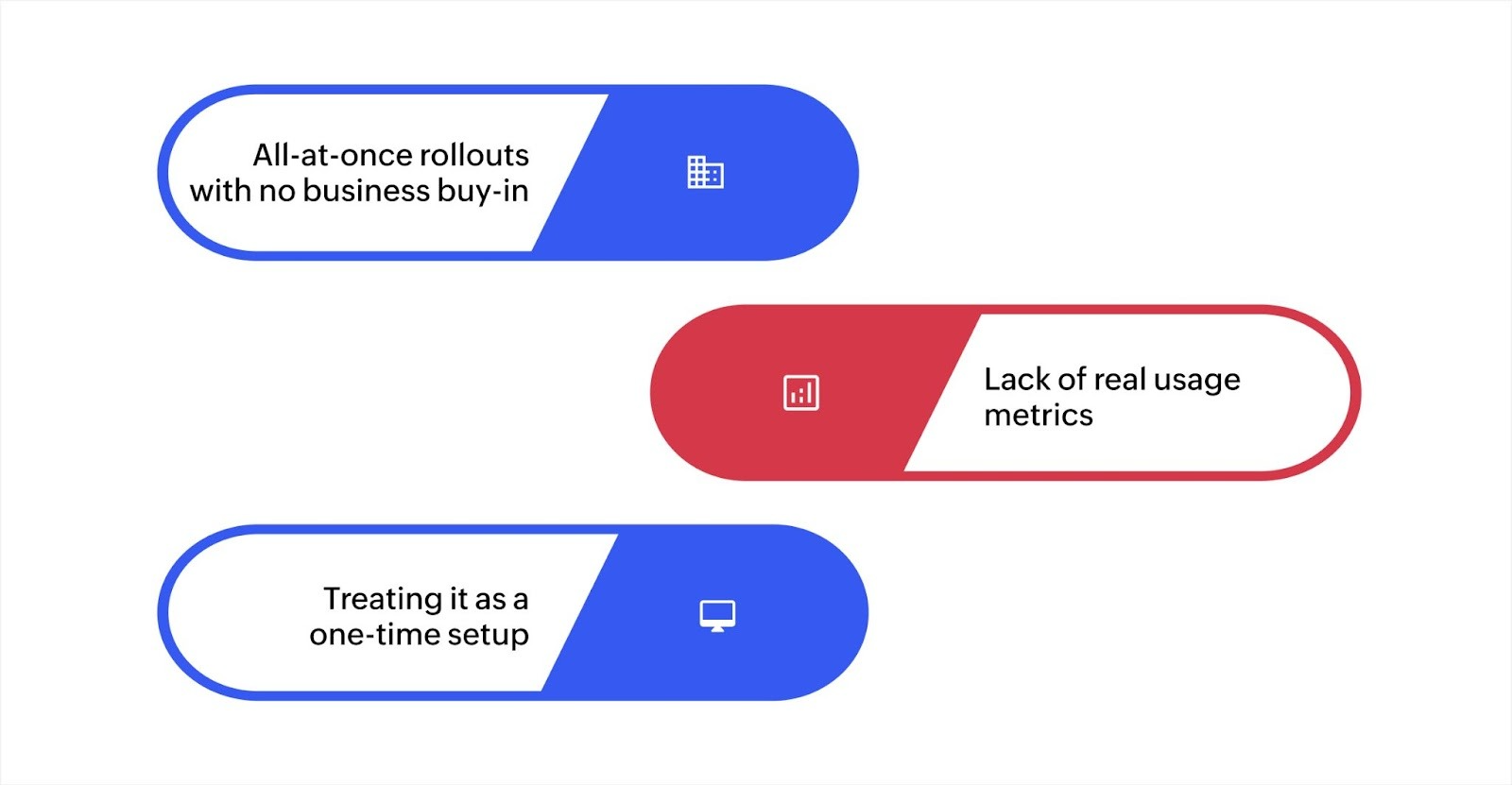
All-at-once rollouts with no business buy-in
A common pitfall in implementing application governance is attempting an all-at-once rollout. This approach often results in resistance from key stakeholders, limited adoption, and disruption to ongoing operations.
Instead, it’s more effective to take a phased, gradual approach. This ensures that all relevant stakeholders can contribute to a smooth and successful implementation.
Lack of real usage metrics
Without tracking real usage metrics, it’s difficult to measure the effectiveness of governance policies.
Governance frameworks should include metrics such as compliance conflicts to ensure that decisions are data-driven and informed. This helps optimize app portfolios and ensure that governance is actively improving operations.
Treating it as a one-time setup
Another critical mistake is treating application governance as a one-off initiative. Governance should be an ongoing process that adapts to changing business needs.
Regular reviews, audits, and updates to the governance framework ensure that it remains current and relevant.
These challenges are signals. As tech stacks grow, governance needs to evolve with them. The good news? New tools, practices, and mindsets are already reshaping how governance works in modern environments.
Trends to follow in application governance in 2025
As organizations build modern software systems, application governance needs to keep pace. Instead of functioning as a final checkpoint, governance is now being integrated earlier and more deeply across the software lifecycle.
The table below outlines key trends driving this shift and what each means for how governance is managed today.
| Trend | What is it? | How does it help? governance? |
| Artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain | AI is used to automate manual reviews and detect unusual activities. Blockchain creates secure records of system actions. | Builds reliable audit trails for user activity and policy enforcement. |
| New compliance and industry regulations | Privacy, cybersecurity, and digital accountability laws are growing across industries. | Monitors changes, flags violations, and adjusts access controls in real time. |
| DevSecOps (development + security + operations) | Security practices are integrated throughout software development, not added afterward. | Enables early governance checks and faster remediation of policy gaps before deployment. |
| Cloud-native and container-based apps | Applications are now built for cloud environments using containers, making them portable and scalable. | Governance tools must track app usage and access patterns in real-time across cloud services. |
| Automation and machine learning | Automated systems test code, scan configurations, and enforce policies with minimal human input. | Identifies risks and enforces rules across large app portfolios. |
While emerging trends show where application governance is headed, frameworks provide the foundation for putting governance into practice. These models help businesses apply consistent policies, controls, and processes across their application environments.
Application governance frameworks
Most organizations rely on governance frameworks to formalize the maintenance and security of their applications. These frameworks offer structured approaches ranging from enterprise architecture to information security. Here are the most widely used ones.
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology)
Developed by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA), COBIT provides a structured approach to governing IT operations. It breaks IT processes into planning, delivery, implementation, and monitoring stages. In this way, it becomes easier to align software systems with business needs and compliance goals.
TOGAF (The Open Group Architecture Framework)
TOGAF helps design enterprise IT architecture by breaking it down into four layers: business, data, application, and technology. It supports governance by standardizing how applications are developed, integrated, and managed within an organization’s broader architecture.
International Organization for Standardization/International Electrotechnical Commission 27001 (ISO/IEC 27001)
This international standard focuses on information security management. It guides IT teams in protecting data by setting up policies and controls around confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library)
ITIL offers best practices for managing IT services. The latest version, ITIL 4, emphasizes value delivery and governance.
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) cybersecurity framework
Created by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology, this framework strengthens the security side of governance. It defines five key functions, such as identify, protect, detect, respond, and recover. This secures applications against evolving threats.
Together, these frameworks offer a strong foundation to govern applications effectively.
Rethink governance as a living framework with Zoho Creator
Application governance needs to scale with your business. It's about maintaining alignment between your application ecosystem, user needs, and compliance requirements. Modern governance provides oversight while giving you the ability to adapt as things change.
Zoho Creator gives you the tools to build and govern business apps with control and flexibility. You can trigger approvals, monitor app usage, and even enforce periodic reviews, all from one unified dashboard.
Schedule your personalized demo of Zoho Creator today. Explore how it can help you build applications, enforce governance, and scale without chaos.
FAQ
How can application governance improve cross-department collaboration?
Application governance improves cross-department collaboration by assigning clear ownership of applications to different business units. This shared responsibility promotes transparency. It reduces redundancies and enables better decision-making about which tools to adopt.
How does application governance help with scalability?
As your business grows, so does the need for more applications. Application governance ensures that, as new apps are introduced, they’re integrated securely and efficiently. With a well-structured governance framework, scaling doesn’t lead to chaotic app sprawl or security vulnerabilities.
What role does automation play in application governance?
Automation simplifies application governance by reducing manual effort and ensuring consistency. It helps manage application updates and recertifications automatically. This allows businesses to maintain governance while minimizing IT workload.
How can I measure the effectiveness of my application governance framework?
The effectiveness of application governance can be measured using key performance indicators (KPIs) like app usage metrics and access review frequency. Additionally, tracking cost savings from consolidating redundant applications helps assess the financial impact.
 Bharathi Monika Venkatesan
Bharathi Monika VenkatesanBharathi Monika Venkatesan is a content writer at Zoho Creator. Outside of work, she enjoys exploring history, reading short novels, and cherishing moments of personal introspection.