Java SDK for Zoho CRM APIs
The Java SDK for Zoho CRM allows developers to easily create Java applications that can be integrated with Zoho CRM. It serves as a wrapper for the Zoho CRM REST APIs, making it easier to access and utilize the services of Zoho CRM.
Authentication to access the CRM APIs is facilitated through OAuth2.0, and the authentication process is streamlined through the use of the Java SDK. The grant and access/refresh tokens are generated and managed within the SDK code, eliminating the need for manual handling during data synchronization between Zoho CRM and the client application.
The latest version of Java SDK (v2.0.0) supports version 8 of Zoho CRM APIs. For more information on the released JAVA SDK versions, refer here.
Prerequisites
- Ensure that you have a Java development environment set up on your system. with Java version 11 or above.
- An IDE such as Eclipse or IntelliJ
- Zoho CRM account.
Step 1: Register your application
Before you get started with authorization and make any API calls using the Zoho CRM JAVA SDKs, you need to register your application with Zoho CRM.
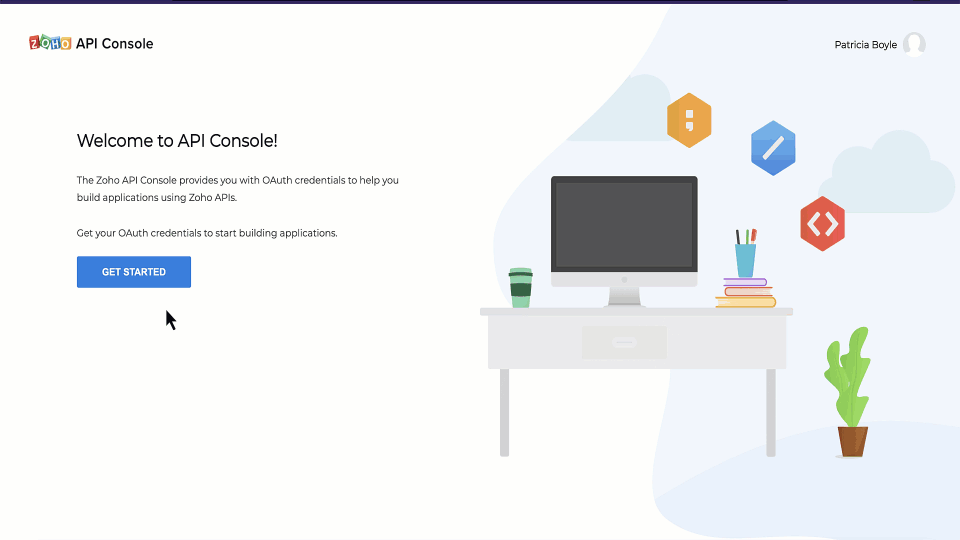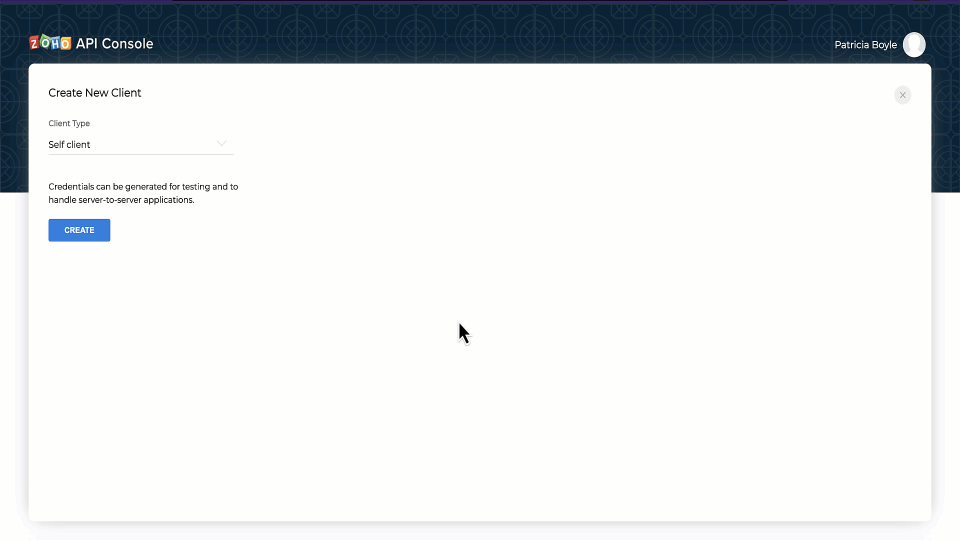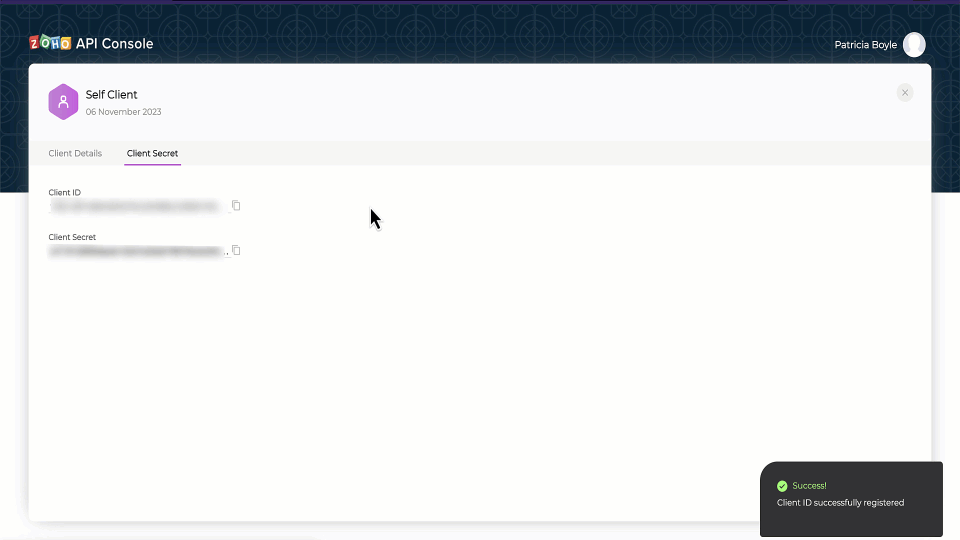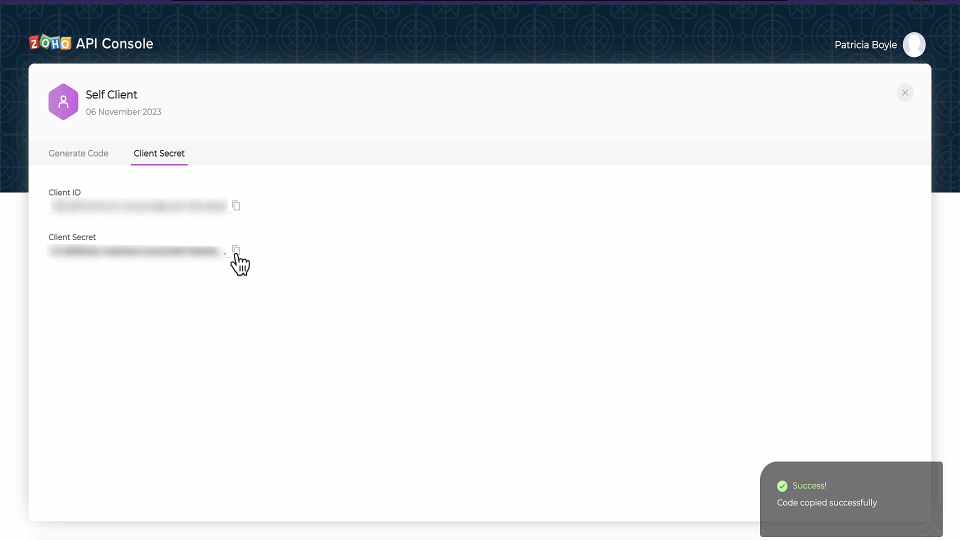
- Go to Zoho API console and click on Add Client
- Choose the client type as Self Client or Server-based Applications depending on your requirements.
- Enter the required credentials.
- Click CREATE
- Make a note of the Client ID and Client Secret generated for your application.
Step 2 : Create a project and add Java SDK and dependencies in your project
In this step, you'll create a new Java project in your preferred IDE. We will be using Eclipse IDE in this guide.
- Create a new Java project in your IDE.
- Add the Zoho CRM JAVA SDK and other JARS to your project as a dependency. Please find the downloadable JARs for version 8 SDKs here. To install Java SDK supporting version 8 if Zoho CRM APIs, install zohocrm-java-sdk-8-0.jar file.
You can also include the SDK in your project using Maven distribution or Gradle. Please refer here to learn more about how to include the Zoho CRM Java SDK in your project.
Step 3 : Generation of Grant token
Generate a grant token from the Zoho API Console by following the steps described in this page.
Step 4: Configuration and Initialization
In the configuration step, you will set up details such as user authentication, environment, token persistence, logging, and API call timeout settings. The following table gives the details of all the keys you can configure, with detailed explanation.
| Key | Description | Sample |
|---|---|---|
mandatory | Represents the domain information to make API calls in Domain.Environment pattern. Domains: USDataCenter, EUDataCenter, INDataCenter, CNDataCenter, AUDataCenter Environments: PRODUCTION(), DEVELOPER(), SANDBOX() | Environment environment = USDataCenter.PRODUCTION; |
mandatory | Contains user token details. Depending on the tokens, you can choose grantToken flow, refreshToken flow, or accessToken flow. | Token token= new OAuthToken.Builder() .clientID("clientId") .clientSecret("clientSecret") .grantToken("grantToken") .redirectURL("redirectURL") .build(); |
optional | Contains the configuration for logging exceptions and API call information. By default, the logs will be available in the workspace as sdk_logs.log. | Logger logger = new Logger.Builder() .level(Levels.INFO) .filePath("/Users/java_sdk_log.log") .build(); |
optional | Contains details for the Token Persistence object. You can choose between DB Store, File Store, or Custom Store and configure accordingly. To know more about token persistence, refer here. | TokenStore tokenstore = new DBStore.Builder() .host("hostName") .databaseName("databaseName") .tableName("tableName") .userName("userName") .password("password") .portNumber("portNumber") .build(); |
optional | Contains additional configuration details like timeout, autorefresh fields, picklistvalidation, etc. | SDKConfig sdkConfig = new SDKConfig.Builder() .autoRefreshFields(false) .pickListValidation(true) .build(); |
optional | The path containing the absolute directory path to store user-specific files containing the module fields information. The field metadata for the current user will be fetched and saved in the JSON file. Whenever a user performs a record operation, the data types, picklist values, unique fields etc in the input will be validated against the field metadata stored in the JSON file. In case the user tries to perform a record operation with wrong pick list values, or wrong datatype, it will be caught during this validation stage, and the SDK will throw an error. This will ensure that credits are not consumed for such operations that would anyway result in a failure. In addition to this, the response will also be parsed in the correct format depending on the data in the JSON file. | String resourcePath = "/Users"; |
For detailed instructions on how to configure the above keys and get started, refer here. Find a sample code for initialisation here.
Note:
- Access and refresh tokens are specific to both the environment (e.g., Production, Sandbox, Developer) and the domain (e.g., IN, CN, US, EU, JP, AU).
You must use tokens only within the environment and domain where they were generated. For example, if you generate tokens in the Sandbox environment under the CN domain, they cannot be reused in the Production environment or in a different domain like US or EU. Attempting to do so will result in an error. - Each API in Zoho CRM has specific OAuth scopes that must be included when generating the token. However, when using the SDK, some APIs require additional scopes to support internal operations such as handling fields, layouts, or related metadata. If any of the required scopes are missing, the SDK will throw an OAUTH-SCOPE-MISMATCH error.
- Deals – Contact Roles API and Records API: SDK additionally needs ZohoCRM.settings.fields.ALL along with ZohoCRM.modules.ALL.
- Related Records API: SDK additionally needs ZohoCRM.settings.fields.ALL and ZohoCRM.settings.related_lists.ALL along with ZohoCRM.modules.ALL.
- Mass Convert API: SDK additionally needs ZohoCRM.settings.fields.ALL along with ZohoCRM.mass_convert.leads.CREATE and ZohoCRM.mass_convert.leads.READ.
Step 5 : Making requests using Java SDK
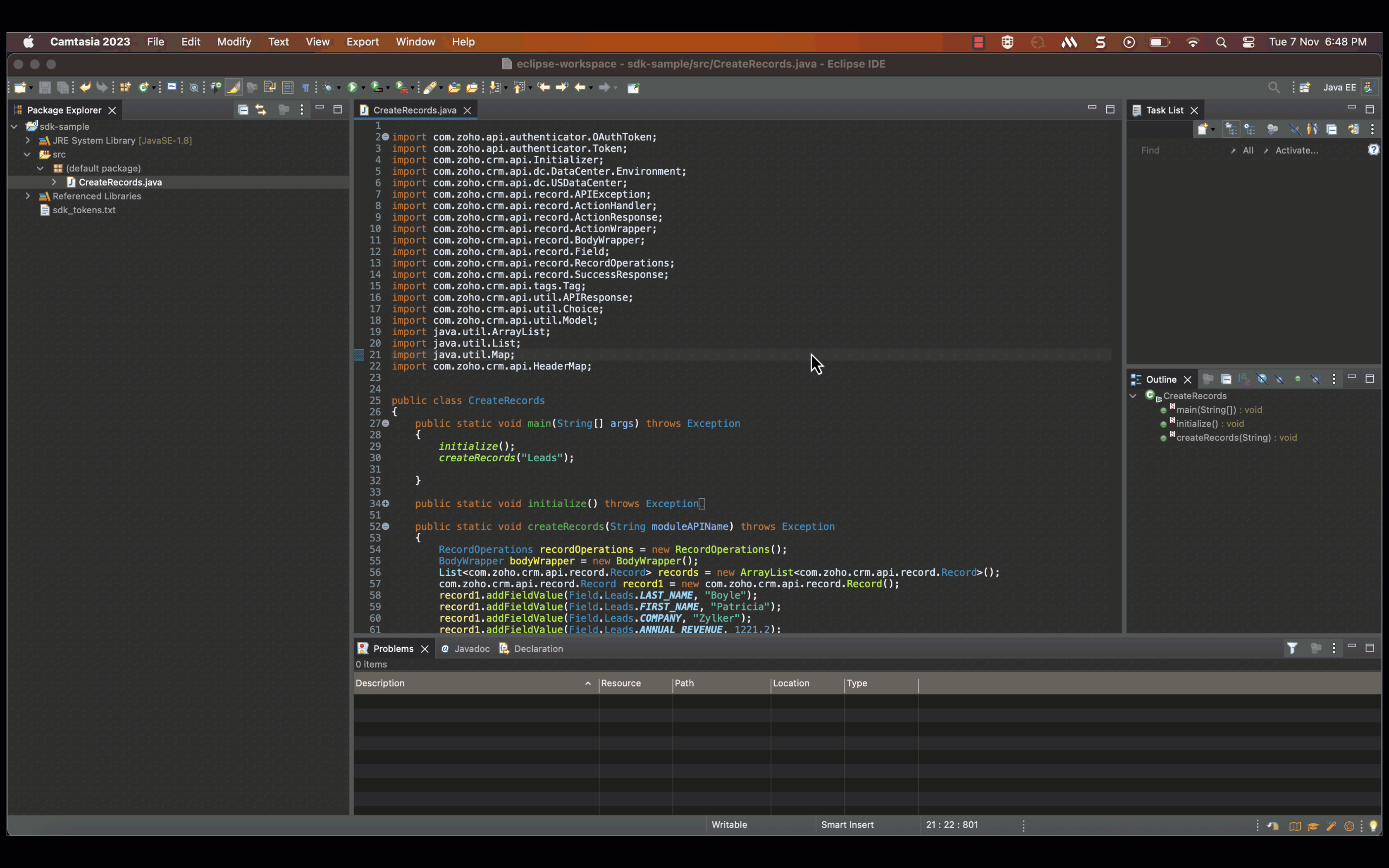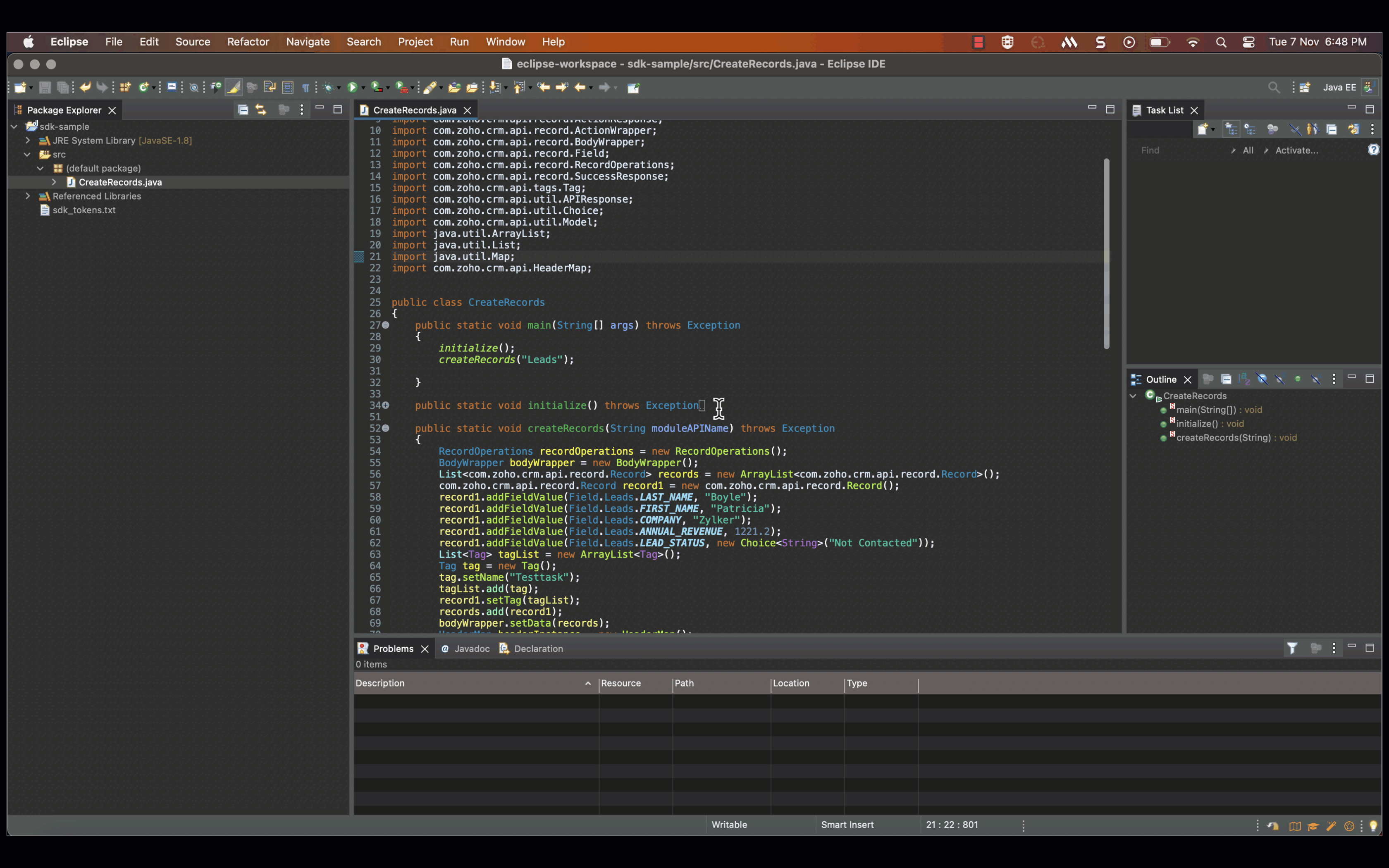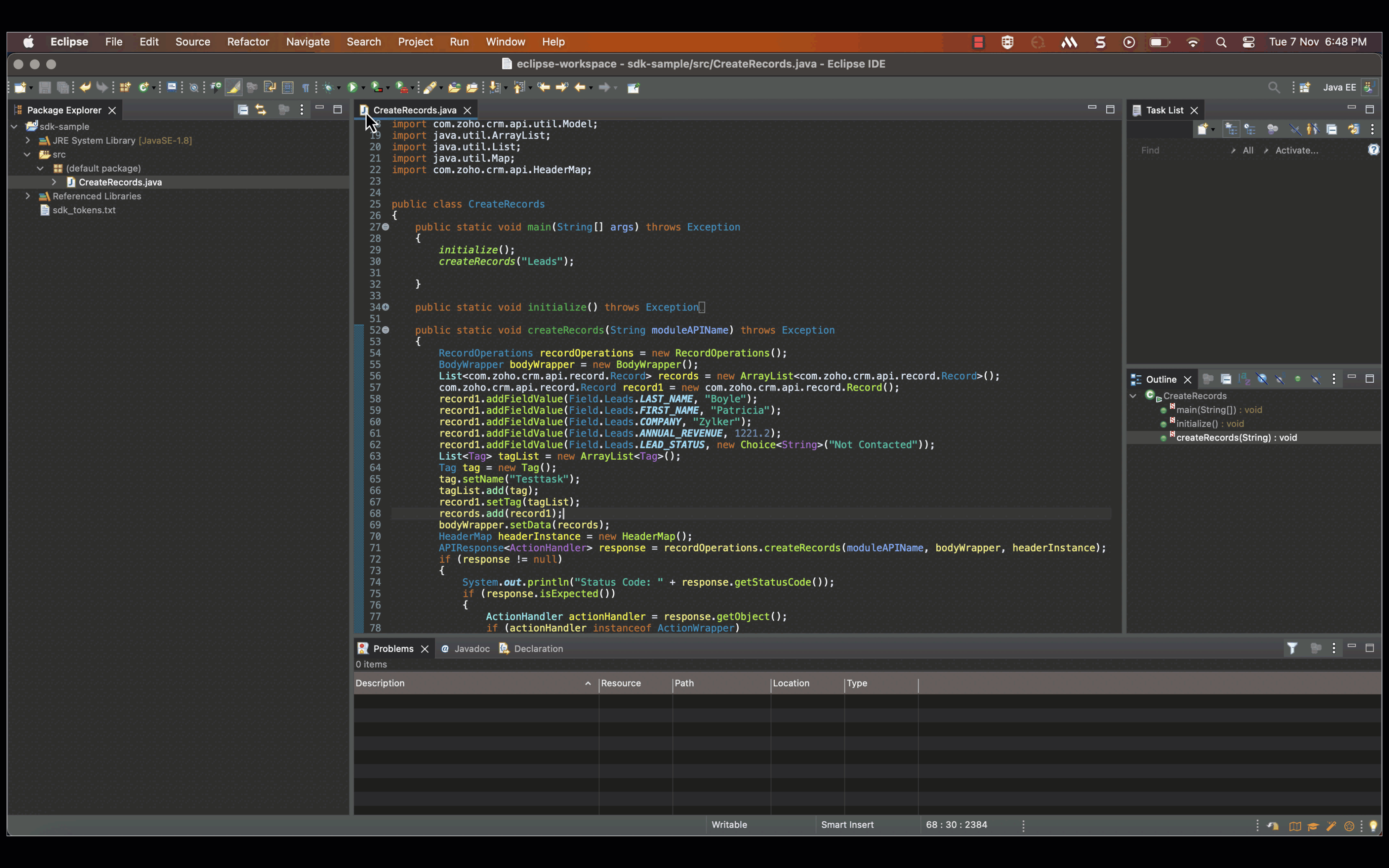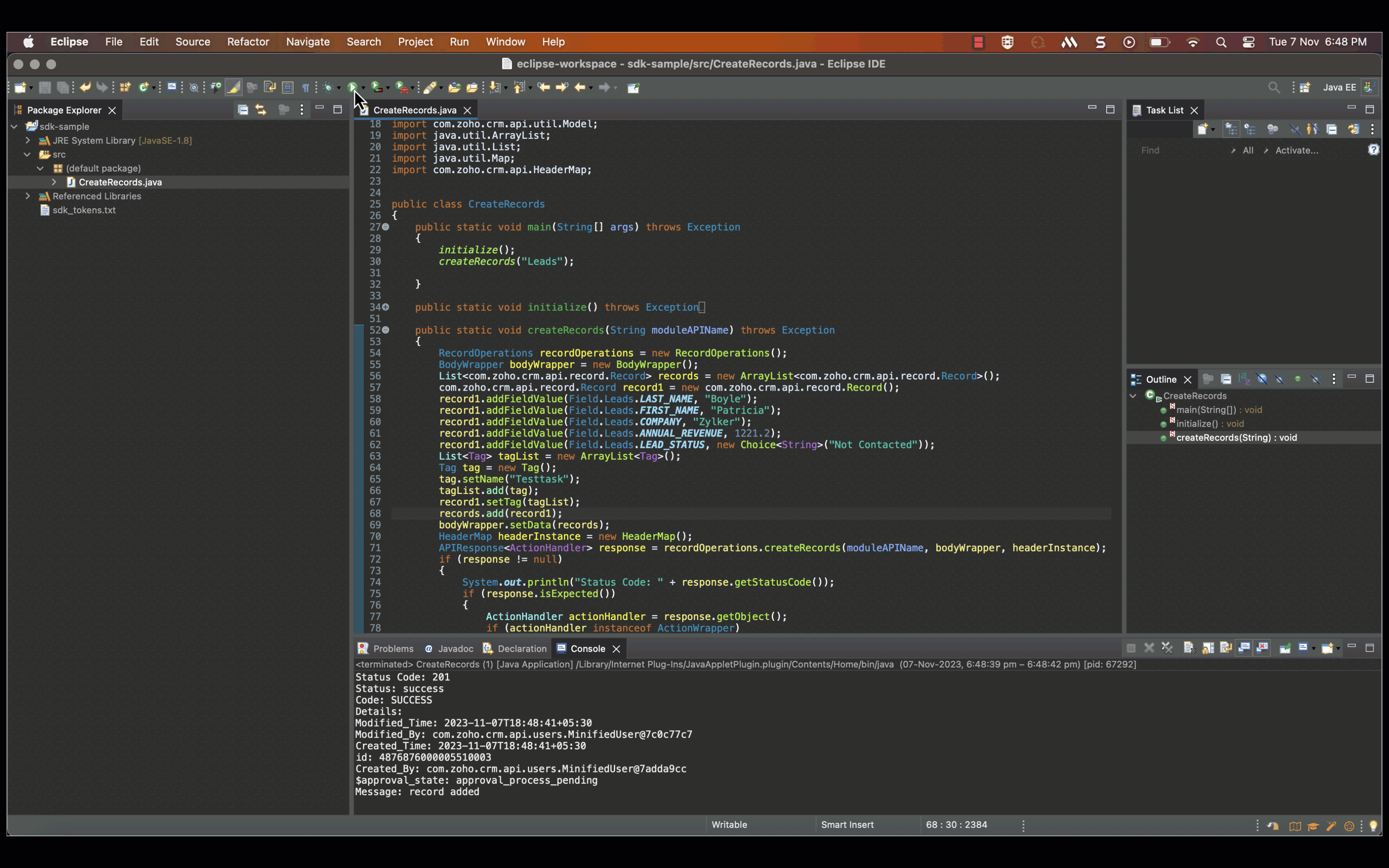
After you have configured and initialised, you can start making your API calls. Here is a sample code to insert a new record in to the Leads module.
Responses and Exceptions
When working with the Zoho CRM Java SDK, it is important to understand the responses and exceptions that can be encountered during API calls.
Note:
- The APIResponse object holds the results of your request. You can access the actual response data using the getObject() method.
- The APIResponse<ResponseHandler>and APIResponse<ActionHandler> are the common wrapper objects for handling responses from Zoho CRM APIs. This depends on the API. For more details, refer here.
- APIException: This exception is thrown for errors that are related to the API itself, such as authentication errors or invalid request parameters.
- SDKException: This exception is thrown for errors that are related to the Zoho CRM SDK, such as network errors or SDK implementation errors.
For more details on the Responses and Exceptions, refer here.